Since the 80’s, in order to make the costs efficient, improve the level of customer satisfactions and expand the scope of participations by employees, companies have been applying business automation systems such as ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning), BPM (Business Process Management), BPO (Business Process Outsourcing) and so on. Since the global economic crisis began, they have been applying lean management system policies to improve the internal business structure, improve the productivity and generate greater outcomes with limited resources. Such activities led to great outcomes in various perspectives such as enterprise advancement and productivity increase and so on, but also marked some poor records in digital functions and innovation leading to new values creation.
Nowadays, along the development of digital technologies, innovative technologies such as AI, cloud, IoT, blockchain and so on are booming in the fourth industrial revolution and amidst the hottest issue of companies called digital transformation, companies are preparing for digital innovation which can help them survive in the future.
Starting with the machine based industrial revolution, the manufacturing site has begun to introduce robots in the factory to substitute for the labor force by humans and support factory automation to maximize the productivity in this smart factory transition. In the office business environment as well, digital weapons to improve the productivity are now applied. Digital Innovation tools used at the office environment is called RPA (Robotic Process Automation), just like the physical robots in the manufacturing site, software robots are substituting for low value-added business by humans and automate the process to improve the productivity so that we can shift to a new business environment where humans and digital workers can work together.
* Lean management: Considering the fact that Toyota’s production system achieves high efficiency despite the low investment costs, and less equipment and space compared to other factories, the lean management policy is applied to inspect the processes (entire processes of material purchase-production-inventory management-sales) and minimize the wastes in the processes. From the new perspectives, waste factors are found and removed to achieve the abilities to resolve issues and improve the competitiveness of the company.
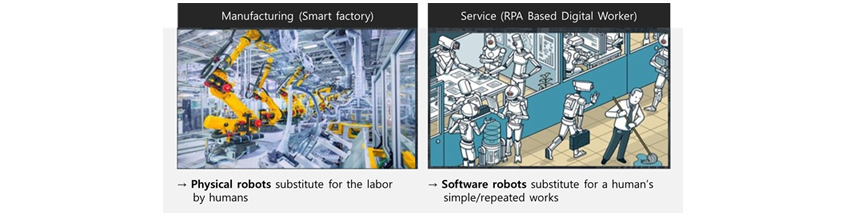 Comparisons of business automation: Manufacturing site and Service office business environment (Source: Samsung SDS)
Comparisons of business automation: Manufacturing site and Service office business environment (Source: Samsung SDS)
Software Robots in the office business environment, Robotic Process Automation
RPA (Robotic Process Automation) is a solution for automating the business that needs to be repeatedly done by a user through the use of software robots, or bot and it is applicable to various tasks such as data input, collection, and email sending: △Frequent and bulk execution tasks, △Tasks performed by many people, △Tasks with frequent human errors, △Simple rules and logic based tasks and tasks with less exceptions, △Tasks requiring access to various systems (ex. Legacy ↔ ERP linking tasks), △Tasks involving processing the standard structure data, △Tasks occurring on specific time periods and so on.
RPA can use software robots (bots) in the automation of standard business to reduce the labor costs and remove human errors and help employees to focus on highly creative business with high added values, so their experiences can be improved and also the productivity can be improved due to non-interruption business for 7 days a week, 24 hours a day. In addition, when it is difficult to improve the large-scale IT systems (ERP, BPM), we can use RPA to connect the systems and process the automated business across the systems.
Let's look at the example of early adoption of RPA technologies in the world, Wall mart, Deutsch bank, AT&T, Ernst & Young, American Express and so on adopted RPA to automate the repeating routine business and replace the direct manpower hiring with RPA to reduce the costs. [1]
- Wall mart: About 500 robots are deployed to automate the entire processes from handling an employee’s question to searches for audit documents and useful information.
- American Express: Using RPA, they are trying to find a way to automate the process of canceling air flight tickets booking and granting refund and also a way to automate the process of auto re-booking recommendation and specific cost management business when an airport is shut down.
Also, in Korea, since the introduction of a 52 weekly working hour regulation, RPA is spreading very widely. Especially, the financial sector that has been granted a 1-year grace period of 52 weekly working hour duties is very much willing to adopt RPA and such a trend is widely spreading to manufacturing business and service industry. Due to the recent crisis of COVID-19, non-face to face business is expanding across various industries and there are increasingly more in-house works. As a result, RPA is newly emerging as technology that can improve the productivity and efficiency through business automation.
According to a customer survey performed by a global Research & Advisory company, Gartner, “The reference customer survey showed that decision makers (typically CIOs, enterprise architects, CFOs and IT leaders) purchased an RPA for these top three reasons:
• Optimize operational efficiency — 90%, with 57% considering that as the No. 1 priority.
• Accelerate an existing process — 46%, with 8% considering that as the No. 1 priority.
• Optimize cost — 43%, with 13% considering that as the No. 1 priority. “ [2]
RPA Market, Main Driving Force for Annual Growth of 25%
According to Fortune Business Insight, “The global robotic process automation (RPA) market size was USD 1.29 billion in 2020. The global impact of COVID-19 has been unprecedented and staggering, with robotic process automation witnessing a positive impact on demand across all regions amid the pandemic. Based on our analysis, the global market exhibited a significant growth of 21.3% in 2020 as compared to the average year-on-year growth during 2017-2019. The market is projected to grow form USD 1.61 billion in 2021 to USD 7.64 billion in 2028 at a CAGR of 25% in the 2021-2028 period.” [3] Besides, according to forecasts by Forrester, “one in every four information workers will receive help from software bots or Robotic Process Automation in 2021.” As organizations began to enter the second year of COVID-19 pandemic, they would want to user RPA and other automation technologies to maintain employees’ great outcomes, participation and efficiency. In 2020, RPA was widely adopted by organizations in 2020, but in 2021, it will mature into a technology meant for every department across an organization.
In 2021, RPA will become one of the hottest technological trends and the main factors for affecting RPA after 2021 are defined as follows. [4]
1. Rise of Intelligent Process Automation (IPA)
IPA (Intelligent Process Automation) is a strong combination of RPA's rule-based automation functions with AI’s preciseness and the machine learning and fundamental process re-design process. It is a new business approach. Thanks to the upswell of RPA adoption on a worldwide scale, organizations are now looking for new ways to take automation further ahead. IPA will deliver them with highly sophisticated, constantly-learning, and ever-evolving smart automation system.
2. RPA as a Service (RPAaaS) will become mainstream
Utilizing the wide popularity of RPA, many automation system integrators are already planning on launching RPA as a Service model. RPAaaS will incrementally decrease development and deployment costs and drive the need for deploying the most impactful and most reusable components.
3. Proliferation of RPA across various Sectors
Now that the transformative value of RPA has been well established, it will witness a major proliferation in various non-technology sectors. While the Healthcare, Government, banking, and various other sectors are already employing RPA in a limited capacity to increase productivity and efficiency, the technology will expand in scope and span in 2021.
4. Gradual Elimination of Paperwork
According to t Research and Markets report, “by 2025 the automation market will be overwhelmed with easy-to-deploy RPA models with pre-constructed functionalities for automating a variety of paperwork in an enterprise”. In the future, paperwork will be history and intervention by humans in the rule-based business will no longer be needed according to our forecasts.
5. Blending of Manual and Digital Efforts
Robots must keep automating the boring and repeating business and some processes requiring human intelligence should be still performed manually. In 2020, to fully automate business process, RPA was implemented but in 2021, we will adopt a more mixed type of approach where humans and robots voluntarily cooperate with each other to perform the tasks. In the future, RPA will be merged with various innovative technologies such as Blockchain, OCR (Optical Character Recognition), advanced data analysis and so on, thus making the automation even stronger.
6. Importance of Employee Experiences (EX) and RPA
As our waiting for COVID-19 vaccine continues, there will be increasingly more interests in employee experiences. Due to our heightened alerts to COVID-19 and the resulting global economic downturns, we can use RPA to maintain the productivity and efficiency of employees and let them escape from the routine business and learn new technologies and contribute to the success of the company.
Out of the six major driving forces for RPA mentioned above, Intelligent Process Automation (IPA) is particularly coming into the center of attention, taking up 11% of official analyst inquiries with RPA at Forrester as shown in the figure below.
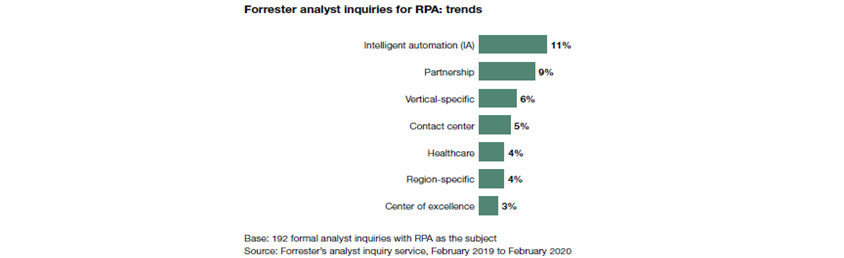 Forrester analyst inquiries for RPA: trends (Source: Forrester[5])
Forrester analyst inquiries for RPA: trends (Source: Forrester[5])
IPA, Intelligent Automation Innovation
Intelligent process automation (IPA) is a robot system beyond RPA that performs simple tasks as it can make its own decisions and perform tasks by combining basic process redesign, process automation (RPA), AI and machine learning (ML). By eliminating repeated tasks, we can help employees and improve the business process and also simplify the interactions and accelerate the process to improve the customer’s journey. IPA initially mimics the business performed by humans but as the time progresses, it will learn how to perform better business. Traditional use of rule-based automation can be improved as a decision-making ability due to deep learning and cognitive technologies. If the current RPA technology focuses on back-office automation while executing the standard business, then the scope of IPA application can be expanded to business that is hard to be standardized or front office business as well.
Gartner mentioned the technology as the hyperautomation concept. Starting with task automation, process/business automation is now merged with technologies such as event handling, conversation UX (chatbots and so on), AI/Machine Learning and so on for hyperautomation.
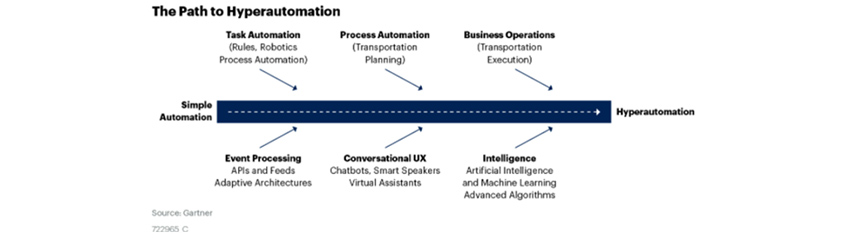 The Path to Hyperautomation (Source: Gartner, The 2020 Top Strategic Transportation Technology Trends[6])
The Path to Hyperautomation (Source: Gartner, The 2020 Top Strategic Transportation Technology Trends[6])
□ Integration of Related Process Automation Technologies
Technological factors for evolution toward IPA are defined in various ways within the market but the contexts are very similar to one another.
According to a global Research & Advisory company, Gartner, “Product leaders focused on the emerging technologies’ impact on their product and services should:
- Focus on the integration of related process automation technologies
— process mining*, machine learning, analytics, iPaaS*, iBPMS* and decision modeling
— to RPA platforms to enable hyperautomation, rather than make evolutionary changes to existing capabilities of RPA.” [7]
Recently, process mining has newly emerged as key technology factor as it is becoming critical for companies to identify an automation candidate and set the priority accordingly.
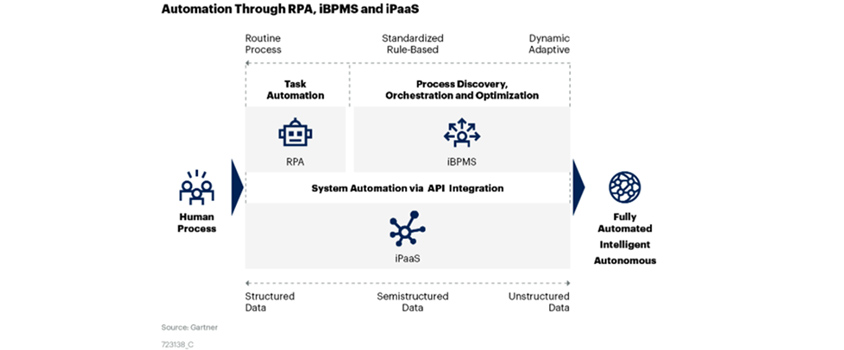 Automation Through RPA, iBPMS and iPaaS (Source: Garter, 2020, Hyper automation Technology Toolkit for Organizations [8])
Automation Through RPA, iBPMS and iPaaS (Source: Garter, 2020, Hyper automation Technology Toolkit for Organizations [8])
Additionally, let’s take a detailed look at the technological factors of IPA defined by McKinsey. [9]
1) RPA: Software automation tools that can automate routines business through the existing user interface such as data extraction and arrangement and so on Robots perform rule-based business such as email and system access, calculation, document and report preparation, file checkup and so on.
2) Smart workflow: Process management software tools that can integrated tasks performed by humans and software robots. A user can initiate the process and track it in real time while software can manage handoffs between humans and robots and provide the statistical data on bottlenecks.
3) ML/advanced analytics: Algorithms that identify patterns in structured data, such as daily performance data, through learning. Machine learning and advanced analytics provides insights based on learning to support compliance, cost reduction, competitiveness and so on.
4) Natural-language generation (NLG): Software engines that create seamless interactions between humans and technology by following rules to translate observations from data into prose. Structured performance data can be piped into a natural-language engine to write internal and external management reports automatically.
5) Cognitive agents: Technologies to build perfect virtual workforce that can combine ML and NLG to perform tasks, communicate and learn data and even make a decision based on emotion detection. (Used to support employees and customers over the phone or via chat, such as in employee service centers)
* process mining: Process mining is designed to discover, monitor and improve real processes (i.e., not assumed processes) by extracting knowledge from event logs readily available in today’s information systems. Process mining includes automated process discovery (i.e., extracting process models from an event log). [7]
* iPaaS (integration platform as a service): “iPaaS is an ideal solution to rapidly automate processes that use existing APIs or software interfaces.” “Integration platforms are effective at orchestrating a series of interactions by software systems, where no human involvement is required.” [8]
* iBPMS(intelligent business process management systems): iBPMS offer a faster and more agile development environment while continuing to focus on enterprisewide process discovery, visualization and monitoring. An iBPMS combines low-code application development, an integration platform and process workflow into a single package. [8]
□ E2E Process Automation Revolution and Transition to Cloud
Companies will focus their investments on technologies to make the operation efficient. They can also provide workers with supporting service to improve the working speed and efficiency or identify mistakes ahead of time and immediately improve them after they are found, thus eventually ruling out the possibilities for mistakes. This will enable us to achieve more dynamic automation through IPA.
IPA combines RPA’s simple business execution abilities to more intelligent automation technology factors, in other words, the analysis abilities shown in the automation process discovery, machine learning and analysis function, and cognitive technologies such as computer vision, NLP (natural language processing) and fuzzy logics to further widen the scope of application for business process automation, thus eventually achieving human-robot collaboration in the entire process of automation (search-automation-optimization), supporting automation of end to end business processes and accelerating the digital transformation. Amidst the COVID-19 crisis and market turmoil, the fact is well verified by a sudden increase in the early investments on the RPA companies focusing on end-to-end process automation solutions for venture capital in 1Q of 2020. [7] It can facilitate E2E digital process operation where RPA, chatbots, cognitive technology and other various digital transformation technologies are merged with each other to design a series of workflow and seamlessly connect the key processes of companies, thus maximizing free data flows and efficient collaboration.
COVID-19 has shown us the desperate needs for a transition to the cloud environment. Due to COVID-19, they could commute to offices and also could not operate systems or expand its capacities and there was no way for them to help the system easily adapting to the changes. Cloud based automation can resolve most of the issues. There will be still some crisis due to environmental changes after the COVID-19 is over and increasingly more employees will work at home. The needs for better adaptation and availability will accelerate a transition toward cloud and hybrid IPA services.
IPA at the Center of Digital Transformation
As global companies experience COVID-19 in the globe, they are trying to improve the business response abilities and support various types of business by accelerating a digital transition that can improve the business efficiency and competitiveness.
The scope of business automation by companies has been expanding mainly due to the needs for intelligent automation in the past several years. As AI (Artificial Intelligence) and machine learning technologies advance, there are increasingly more changes made in a way machines and humans interact with each other, and cognitive technologies, data analysis methods and decision making, and as a result they are enforcing digital innovation through smart business process/workflow where robots think, learn and apply on their own. In other words, AI (especially machine learning) can be used for automation and intelligent decision making so that sufficient flexibilities are provided in an end-to-end process that integrates different systems.
The main goal of intelligent automation is to revolutionize the customer and employee’s experiences and improve the productivity. By saving time and costs, companies can minimize human interventions in the simple, repeating business process and let them focus on more valuable tasks such as conversations with customers, business planning and development, new business proposal and so on and also improve the end-to-end customer experience and finally companies can improve efficiency and save costs and create new values through customer satisfaction, thus achieving the highest competitiveness. In 2021, we will be able to create a digital workflow with competitiveness through IPA beyond RPA and successfully automate the mission critical business.
Learn more about current RPA trends in Gartner's 2021 Magic Quadrant for Robotic Process Automation.
# References
[1] https://www.cio.com/article/3236451/what-is-rpa-robotic-process-automation-explained.html
[2] Gartner, Magic Quadrant for Robotic Process Automation, Cathy Tornbohm, et al., 27 July 2020
[3] https://www.fortunebusinessinsights.com/robotic-process-automation-rpa-market-102042
[4] https://agreeya.com/6-top-trends-for-robotic-process-automation-rpa-in-2021-beyond/
[5] Forrester, RPA Inquiry Spotlight, 2020, Forrester Inquiries Highlight Scale, Security, Governance, And AI Integration Issues
[6] Gartner, The 2020 Top Strategic Transportation Technology Trends, Bart De Muynck, 9 June 2020
[7] Gartner, Emerging Technologies Venture Capital Growth Insights: Robotic Process Automation, Arthur Villa, et al., 4 February 2021
[8] Gartner, Hyperautomation Technology Toolkit for Organizations, Finance Research Team, 24 April 2020
[9] https://www.mckinsey.com/business-functions/mckinsey-digital/our-insights/intelligent-process-automation-the-engine-at-the-core-of-the-next-generation-operating-model#
[10] https://www.digitalistmag.com/cio-knowledge/2020/01/06/creating-business-value-with-intelligent-automation-06202044/
Disclaimer*: Gartner does not endorse any vendor, product or service depicted in its research publications, and does not advise technology users to select only those vendors with the highest ratings or other designation. Gartner research publications consist of the opinions of Gartner’s research organization and should not be construed as statements of fact. Gartner disclaims all warranties, expressed or implied, with respect to this research, including any warranties of merchantability or fitness for a particular purpose.

Strategic Marketing Team at Samsung SDS
Had been in charge of digital transformation in samsungsds.com, solution page planning/operation, based on her work experiences in IT trend analysis, process innovation, and consulting business strategy, and is now in charge of content planning and marketing through trend/solution analysis for each main business sector of SDS.
- Inteligência de Decisão Potencializada pela Hiperautomação
- Case Study: Samsung Biologics Automates Generative AI-Based Works
- A Comprehensive Collaboration Suite to Optimize Digital Employee Experience
- Strategies for Building an Enterprise Document Streaming Service
- Brity RPA on a Mission to Rescue the Financial Industry from Repetitive Tasks!
