CX perspective What is the smart factory? Factories are no longer infrastructures but services

![[Series] Customer Experience Innovation Report (Part1), Smart tactories producing customized products beyond improving productivity](https://image.samsungsds.com/en/insights/smart-factory_eng.jpg?queryString=20230710033030)
“Can smart factories kill two birds with one stone?”
In the past, smart factories mainly focused on the efficiency of providers, including productivity improvement, defect rate reduction, cost reduction, and short delivery time. Ultimately, however, technological advances such as cutting-edge technology and hyper-connected networks enable smart factories to not only improve production efficiency for manufacturers, but also produce customized products for customers. Factory as a Service (FaaS) to be introduced in this article is a notable example.
Factories are no longer infrastructures, but services
Thanks to miniaturized 3D printers, stores now can act as factories, making customers’ purchase experience more innovative. This allows process innovation to take place where customers buy custom-made products at the store right away without having to wait for them to be produced at the factory. Customer-centric manufacturing services are expected to create new experiences that will bring greater joy and satisfaction to customers.
Background of FaaS
What causes this change in manufacturing? The most prominent reasons for inducing these changes in the manufacturing industry are intense competition between companies to be selected by customers and increasing consumers’ tendency for expressing their preferences. Furthermore, with the development of various technologies, the factories no longer need to operate in a centralized manner.
Uses cases of FaaS
A Manufacturing service producing products customers dream about
Now you can have your product made with the customized design, material and size, and quickly buy at the price of mass production. Let's take a look at some of the matters that smart factories need to consider and prepare in terms of digital experience for better communication with customers.
Case1. Speed Factory
Purchasing customized products at an affordable price
A global sports apparel company, A, moved its production plant in Southeast Asia to Germany, introducing automation and robot technology to its manufacturing site, and named it Speed Factory. Robots making shoes and a handful of managers worked together to break down the walls of production and distribution, while saving expenses such as labor costs. With Speed Factory, customers can make their own unique products. How has people's experience changed through company A's smart factory? Let's look at it from different perspectives: consumers, product planners, and executives.
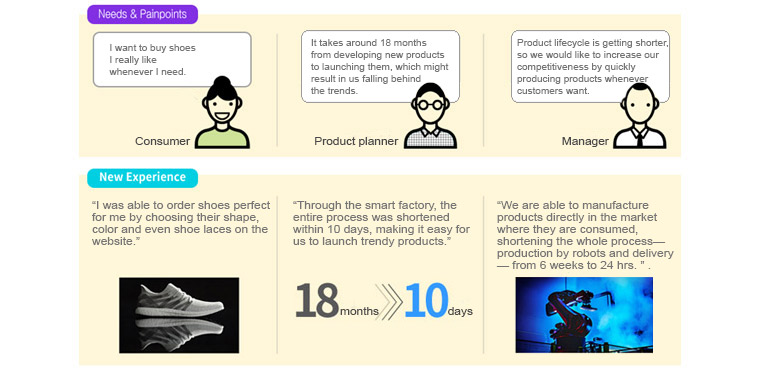
Case2. Build Your One-of-a-kind Harley
Smart Factories making products reflecting customers’ tastes
Company H, a world famous motorcycle manufacturer, has a smart factory that produces products tailored to customers’ tastes. When customers choose the colors and parts they want on the website, the smart factory in York receives the orders and begins manufacturing motorcycles with 1,200 different configurations. The smart factory makes a new bike every 80 seconds. All work procedures are standardized and all workers need to do is assemble the parts, following the instruction screen in front of them. How has people's experience changed through company H's smart factory? Let's look at it from different perspectives: consumers, product planners, and executives.
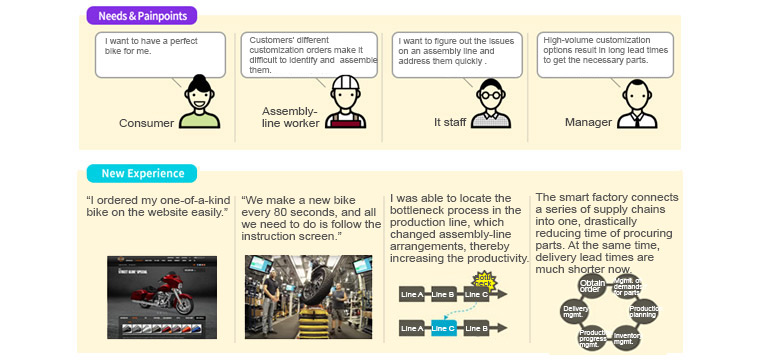
Considerations on FaaS
Through the use cases above, we would like to summarize the needs and pain points of producers and consumers at each stage of production, and take a look at the direction of changes in manufacturing system for buying tailored products and reducing production costs, and considerations in accordance with the new manufacturing process.
Consideration1. Stakeholders’ Needs by Production Stage
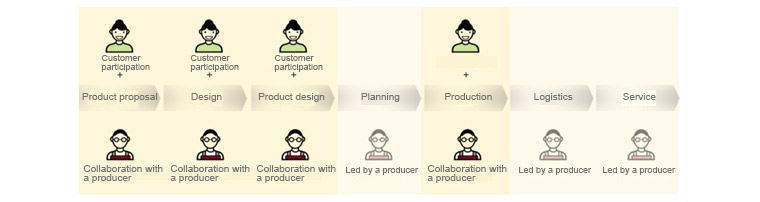
Production stages in traditional manufacturing can be roughly divided into three stages. Consumers should be actively engaged in the production stage, and the decentralization and autonomy of the factory should also take place, while considering the needs and pain points of consumers / producers at each stage.
Consideration2. New Manufacturing Process
As a result of the change, the production stage of the manufacturing sector is further subdivided, and at each stage, the consumer’s participation increases and the role of the producer changes.
Consideration3. System Design Considerations
We have examined the process of the implementation of FaaS as the center of manufacturing has shifted from producers to consumers, and factories have decentralized. In a changing environment, the manufacturing system must be able to satisfy all stakeholders, including users. From the consumer’s point of view, experience in buying the personalized product should be improved and the producers’ experience in satisfying their consumers, while reducing production costs should be enhanced.
Consideration4. Direction of Development Strategy for Digital Experience
To address the consumer / producer needs discussed earlier, manufacturers must make strategic changes in three areas: high-performance, proven & prebuilt, and easily adaptable.
High-Performance
: Provide quick and accurate progress status and the pace of work in direct order production
Easily Adapable
: Provide production-related machine control manuals that customers can produce directly regardless of their proficiency
Proven & Prebuilt
: Provide intuitive information so that customers can accurately understand the ordering options and easily choose
: Easy to modify when the wrong option is selected
In the next part, we will look at best practice cases of manufacturing systems that are more responsive to changes and detailed considerations.
▶ The contents are protected by copyrights laws and the copyrights are owned by the creator and Samsung SDS.
▶ Re-use or reproduction as well as commercial use of the contents without prior consent is strictly prohibited.

Samsung SDS’s CX Team, Service Design Research Group conducts research on experience innovation and changes in experience and appealing point of various stakeholders by ICT development and environment change from a new perspective.
- Four Big IT Transformations for Enterprise Agility
- An Agile Approach, the Core of Corporate DT for Working Culture Innovation
- Digital ESG, a Critical Success Factor for ESG
- Conversational AI War Begins. Who Will Be the Winner?
- What Is Matter, the New Smart Home Standard?
- 2023 Forecast for Technology Trends