1. What on Earth Is Blockchain Technology?
What Is Blockchain Technology?
For those who won't be satisfied if too easy terms are used, let's take a close look at the Blockchain technology using some IT terms.
Blockchain is a data storage technology that creates blocks of a certain unit for continuously growing information and chain-connects them in an effective network. It is operated in systems all around the world in the form of the 'distributed public ledger' without the central system.
The distributed public ledger configured with this Blockchain is open to anyone to access and view the contents up to now from the beginning and add contents additionally. However, the content to be added can be finally written only if its integrity is verified. If once written, nobody can modify or delete it.
Blockchain Structure
Each system (from all around the world) participating in the Blockchain has its distributed public ledger individually without a specific central system. And such a system is called a 'node' of the Blockchain.
The ledger owned by each node is configured with blocks that contain all the data history, and blocks of each ledger are chain-connected in the time series of confirmed transactions. Moreover, since all the nodes contain identical data ultimately, individual forgery on a certain content is virtually impossible.
Automatic Blockchain Synchronization
New information generated on a node of the Blockchain is automatically verified with each other and written on the distributed public ledger by the system and it is automatically synchronized with ledgers of all the nodes all around the world.
The content of the ledger containing the confirmed final block is finally propagated identically to all the nodes by the computerized arithmetic operation that solves the problem according to the mathematical algorithm.
The distributed public ledger writes final information only confirmed by the mutual integrity verification process conducted during the synchronization process.
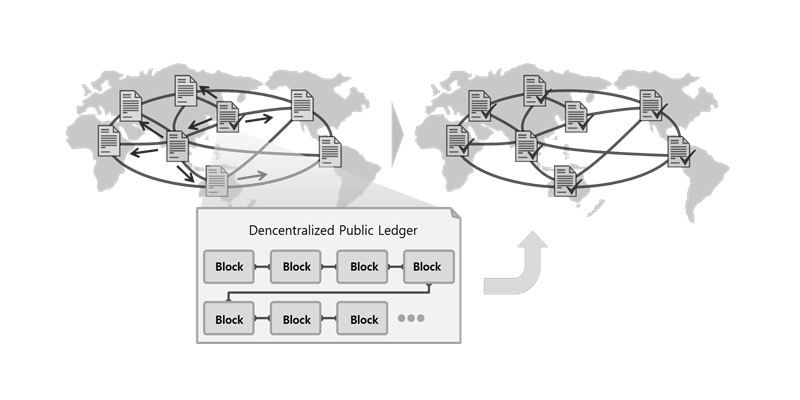 [Figure 1] Automatic Synchronization of Chain-Connected Distributed Public Ledgers
[Figure 1] Automatic Synchronization of Chain-Connected Distributed Public Ledgers
Creation of New Block in a Blockchain Ledger
New transaction information to be written on the distributed public ledger is verified by the algorithm and recorded in a new block in the order of generation.
Each block of the Blockchain contains transaction information at the time as well as the past block information. Each block is connected to each other by using the 'proof of work' of the past block as an 'ID'.
A certain value which satisfies the hash value created by the mathematical algorithm is derived from inputs of new transaction information and past block information, and its result is called the “proof of work”1).
The node that derived the value first notifies the neighboring nodes in the network that a new block is completed, completing creation of a new block.
Besides, this creation method of the Blockchain is the very fundamental reason of the increased security of the Blockchain.
In other words, the reasons are as follows:
Since the past transaction information for which the integrity has been ensured by confirming the transaction information is used as an input, information not yet generated cannot be written; and if the information of a past time is falsified, all the blocks after the time that should use the information as an input should be newly created again, so forgery blocks cannot catch up with normal blocks made longer for continuously generated transactions even at the moment blocks are newly made again by forgery.
2. Opportunities and Risk Factors of Blockchain
What Are Opportunities and Risk Factors of Blockchain?
However, does this unfamiliar topic so called the Blockchain present us the rosy future only? Are there no risk factors or weaknesses in the Blockchain?
In the next section, let's examine both the opportunities and risk factors, then its advantages to be taken and points to be supplemented for the banking industry to utilize it.
Opportunities of Blockchain
The Blockchain has advantages such as reliability, security and speed due to decentralization through the distributed public ledger.
• With information management by the distributed public ledger, information is reliably recovered even if some of the information is lost.
• High security in the sense that past and future transactions cannot be falsified
• Fast speed since centralized management and intermediate links are not required
• Transparency in the sense that all the transaction history can be viewed at a glance
Risk Factors of Blockchain
On the other hand, since there is no centralized management, the contingency plan should be considered.
• In case that the whole system moves toward a wrong direction, a contingency plan is required since there is no centralized management.
• If multiple processing capabilities can be secured beyond a certain level above performance of the whole system, it is theoretically possible to write arbitrary information.
• There is a lead time required for new block creation and synchronization of the entire Blockchain.
Measures to Supplement and Remove Risk Factors of Blockchain
To make up for weaknesses while utilizing advantages, you need to review and make up for the Blockchain technology, which is an open source technology, according to the purposes and requirements of banking system.
• Lack of centralized management: Complement the system to provide a contingency plan through conditional branching and monitoring control on information in blocks.
• Presence of lead time: There are multiple technologies to reduce the lead time by improving algorithms.
3. Opportunity of Blockchain Application on Banking Industry
Opportunity of Blockchain Application by Banking Business Types
There are various Blockchain-based opportunities for business innovation by business applications of each business domain.
First, the common areas that can be applied with the Blockchain include goods, customers, information analysis, management support, etc.
Also, it is possible to use the Blockchain for business innovation on specialized businesses, such as contracting, compensation, funding, banking and trading, carried out by companies such as life insurance, fire insurance, card, securities, etc.
Common Areas
Businesses in the banking industry can be innovated by applying the Blockchain to electronic signature and forgery prevention of documents and client-user authentication.
• Electronic signature and forgery prevention of documents: You can enhance document security through innovation of peer review process on internal electronic documents, reinforced history management, and irreversible electronic signature and forgery prevention.
• Client-user authentication (replacement of digital certificates with the Blockchain): With the Blockchain and the FIDO biometric authentication, you can strengthen the authentication system and raise the service level, and in turn, you can save the cost paid to third-party digital certificate providers.
• Information integration of global head office and branch offices: Using the Blockchain, you can integrate information of the head office, branch offices and overseas affiliates.
Insurance Area
For insurance companies, you can enhance integrity and speed and remove duplicate services by combining contract management and compensation business into the Blockchain.
• Insurance contract-accident-compensation link management: You can enhance information integrity and speed and remove duplicate services by linking contract/accident/compensation information between the insurance company and third party companies using the Blockchain.
• Card area: For the card company, you can utilize the Blockchain for innovation of businesses such as card issuance review, prepaid card, overseas point remittance/settlement, document security, etc..
• Prepaid card issuance, payment, and settlement: You can provide new digital experience to customers by leveraging mobile customer contact opportunity (for instance, Samsung Pay) for prepaid card issuance, settlement, and remittance.
• Issuance review and transaction authorization: You can apply the Blockchain in areas using peer review and transaction block limit check.
• Receivables management and funding: You can promote the use of Blockchain in the banking sector to innovate the ways of performing receivables management and funding for the card companies.
Securities Area
For securities companies, you can apply the Blockchain for innovation of businesses such as prepaid card and point remittance/settlement, non-face-to-face authorization, document control, etc.
• Smart banking account management: You can manage smart accounts for deposit, withdrawal, payment, and remittance.
• Trading and marketable securities management: This area can be fully implemented when the Blockchain is introduced to the stock exchange. It is already possible to manage unlisted companies (for instance, NASDAQ Linq model).
• Smart contracting: You can implement automatic non-face-to-face transaction processing and smart contract/escrow.
• Future market trend analysis and forecast: This is a potential area that can be applied with the Blockchain when agreement is made based on user participation (for instance, Augur model).
4. TOP-B : Samsung SDS's Banking Blockchain Architecture Model
TOP-B stands for trusted operational private Blockchain model.
As mentioned above, there are various business and technical requirements to solve and supplement in order to apply the Blockchain to the banking industry.
Among those, the most important things are to configure the data network based on private Blockchain that satisfies the requirements of the banking industry and to integrate it with various business applications, channels, security and analytics components required by banking companies.
To meet the requirements, Samsung SDS has defined an architecture model based on private Blockchain and has materialized various banking innovation models.
Samsung SDS's TOP-B (Trusted Operational Private Blockchain) architecture is mainly composed of ① security area such as FIDO capable of multiple biometric authentication, ② CX area that provides the omni-channel customer experience, ③ analytics area that performs real time monitoring and big data analysis, and lastly ④ private data network area based on private Blockchain.
5. Conclusion
Why Blockchain? Do you still write mails on a paper instead of using e-mails?
Up to now, we've reviewed the concept and features of the Blockchain as well as its domestic and overseas utilization trend, and checked the reasons why the Blockchain receives global enthusiasm and focus. In addition, we've reviewed the things to consider to apply it to the banking industry, various applicable opportunity areas, and the business and information system models worth considering at this moment.
When something new appears, it is not easy to clearly understand that it is an opportunity or a risk, in other words, a momentary breeze or a storming flow that will change the world. The Blockchain we are facing now may be a trend that passes away in a moment like a storm in a tea cup, or it may be another mirage that reproduces the bitter pain of past system investment that did not meet the expectation.
However, it is obvious that we have to take a close look at it to know if it is good or bad. In fact, many global banking companies, large ICT vendors and startups are fixing their eyes on the Blockchain.
You can say the advertising copy that was once famous, "When all others say yes, say no" only when you surely know that others are wrong.
Lastly, Ashwin Kumar, Global Product Development General Manager of Deutsche Börse, who participated in a new Blockchain project last December, said6):
“The Blockchain technology won't change the market infrastructure entirely. However, ignoring it is
something like asking 'Why is e-mail needed instead of paper mails?’”
▶ The contents are protected by copyrights laws and the copyrights are owned by the creator and Samsung SDS.
▶ Re-use or reproduction as well as commercial use of the contents without prior consent is strictly prohibited.

Lee Jihwan (jihwan.rhie@samsung.com) is a senior consultant for Samsung SDS Financial Consulting Team. For various corporate and institutional clients mainly in financial business, he has successfully completed projects in many different fields ranging from strategy and IT consulting, such as new business and IT strategy establishment using new innovation technology, company-wide architecture design, and system implementation to system development. Currently, he is responsible for the architecture, development, and delivery of Nexledger, an enterprise Blockchain platform for Samsung SDS.
Park Jaehyeon(aldira.park@samsung.com) is a senior consultant for Samsung SDS Financial Consulting Team. He has been doing consulting for over twenty years to propose alternatives to various financial companies' needs. He has been focusing on digital changes that are leading innovation in the financial industry and fields that are applied to practical industry.
- An Enterprise NFT, How to Use It, and How to Develop It
- NFT, Would It Be Used for Anything Other than Collecting?
-
[Technology Toolkit]
Easy and Simple Blockchain Management, Nexledger! - Introducing Maritime Blockchain Project to World Customs Officers
- Samsung SDS’s Blockchain Platform Nexledger Goes Global Beyond Korea
- [Video] What Can Nexfinance™ Do for You and Your Business?
