Damages of Media Forgery and Companies that Offer Forgery Prevention Technologies

Today, we will look at some notable examples of media forgery, and examine areas where forgery prevention technologies can be applied as well as the rival companies that competes in this field.
Cases of Damage from Forgery
In the case of forgery, there have been an increasing number of cases in which photos/videos are fabricated or the picture of others are exploited for illicit gains. Also, fake news containing false information are often spread online, which wreaks damages on individuals, companies or nations.
In Korea, a number of subcontractors have been caught for falsifying or repeatedly using photos of completed construction sites to unlawfully charge construction fees of around KRW 100 million. In fact, 33 out of 608 construction sites were found to have been involved in such forgery cases. One subcontractor even pasted an image of construction equipment onto a photo of an empty road and used it as an evidence for completing its work. It was also found that Company A duplicated the construction photo of Company B to submit it as its proof document of completion.

Source: Gyeonggi Province News Portal (May 4, '21)
According to the National Industrial Conference Board (NICB), about 5-10% of disaster-related insurance claims were found to be fraudulent. In the case of 2021, up to USD 4.6 to 9.2 billion of insurance benefits were unlawfully claimed through fraud. Similar cases were found when the FBI investigated into the funds used for restoring damages from Hurricane Katrina. Of the USD 80 billion government fund offered to support damage recovery, around USD 6 billion, or 7.5% of the fund, turned out to be insurance frauds.
 U.S. insurance companies face damages from fraudulent insurance claims made through forged images submitted by policyholders
U.S. insurance companies face damages from fraudulent insurance claims made through forged images submitted by policyholders
Source: Disaster Claims Fraud Cost Insurers as Much as $9.2B in 2021 (May 17, ’22)
In August 2020, a huge explosion accident occurred at a factory in Beirut, Lebanon, located in the Mediterranean coast. And back then, fake news fabricating the accident as a missile attack by hostile forces were out in the media.

Source: Doctored videos are already faking the cause of Beirut’s explosion(Aug. ’20, CNN News)
, Doctored videos online appear to fake the cause of Beirut explosion(Aug. ’20)
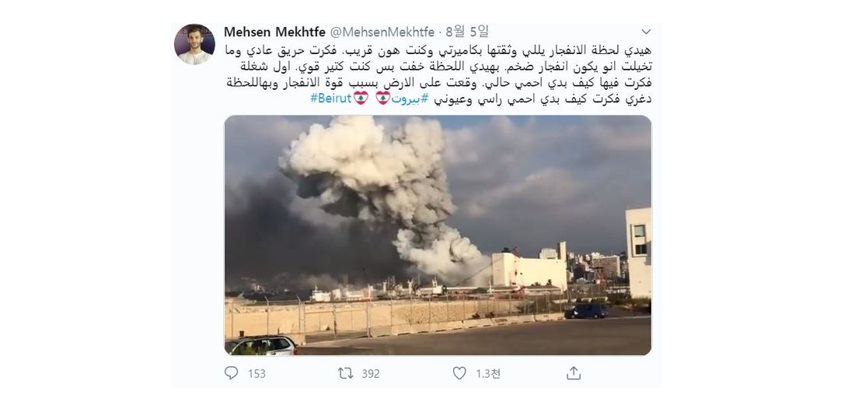
Source: Twit of Mehsen Mekhtfe (CNN Arab SNS Poducer), the first phototaker
As second-hand deals between individuals have become quite common these days, there have been frequent cases of forgery or fraud on Korea's online second-hand marketplaces. As of 2019, the amount of money involved in fraudulent dealings at Joonggonara, Bungaejangter, and Karrot Market (online secondhand marketplace in Korea) stood at KRW 3.5 trillion, KRW 1 trillion, and KRW 0.7 trillion, respectively. At Bungaejangter, there was even a case in which the perpetrator attempted to defraud buyers by editing its ID onto a picture of a second-hand item sold by another person in May 2020.
Then, how does the forgery prevention technology of Team9 works? First, photos taken in real time are sent to the server, while the place and time of shooting the photos are also recorded. Then, the server provides an analysis report on the overall status of falsification on the photos. This process can prevent the occurrence of the abovementioned frauds, and as the technology can also verify the authenticity of a taken photo, users can prove whether a photo has been forged by using the original copy stored safely in the server.
Management of Insurance Refunds on Car Mileage
When signing a car insurance policy, do you perhaps include a special provision regarding car mileage? Special provision on low-mileage discount is an insurance system which allows policyholders to receive cash refunds on their insurance premium if their total sum of mileage from the date of contract signing to expiry is less than the criteria set by the insurance company. It is said that the amount of insurance refunds from mileage discounts is around KRW 1.5 trillion each year. Through the use of Secure Image, insurance companies can proactively block out unlawful insurance claims made by forging the photos of dashboards that are submitted as a proof for receiving mileage discounts.
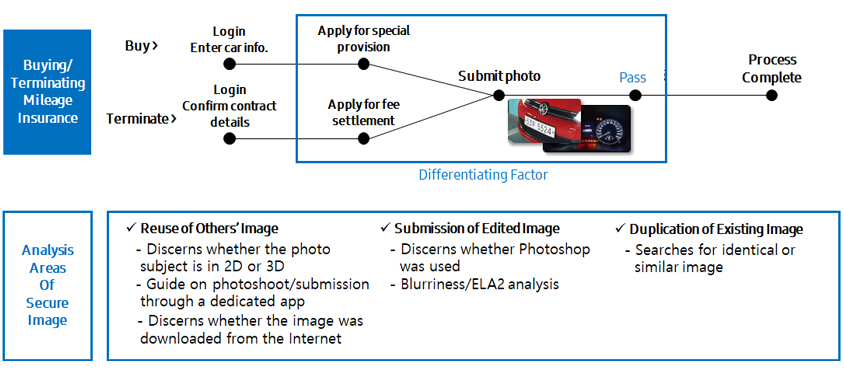
Corporate Asset Management Service
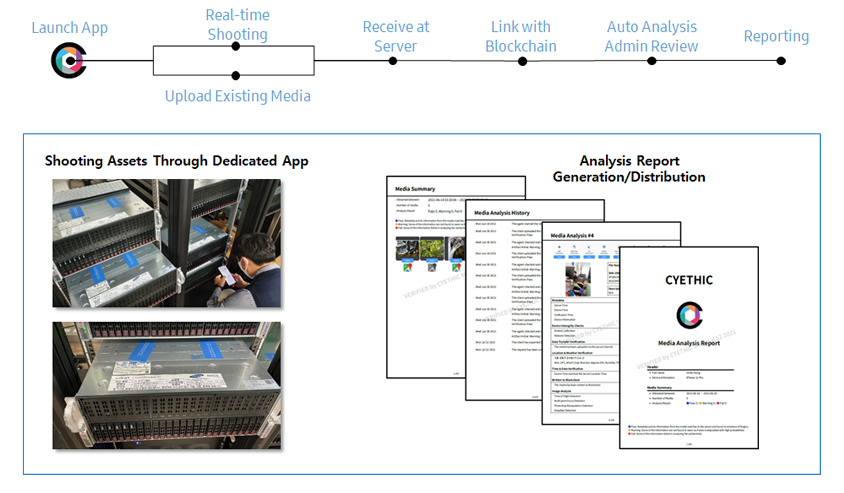
When managing the assets owned by companies, it is critical to identify whether the assets actually exist at their location. Using the technology, the photos of the assets can be taken in real time while such results are stored/printed out in the form of a report, which is highly useful for proving the existence of the assets.
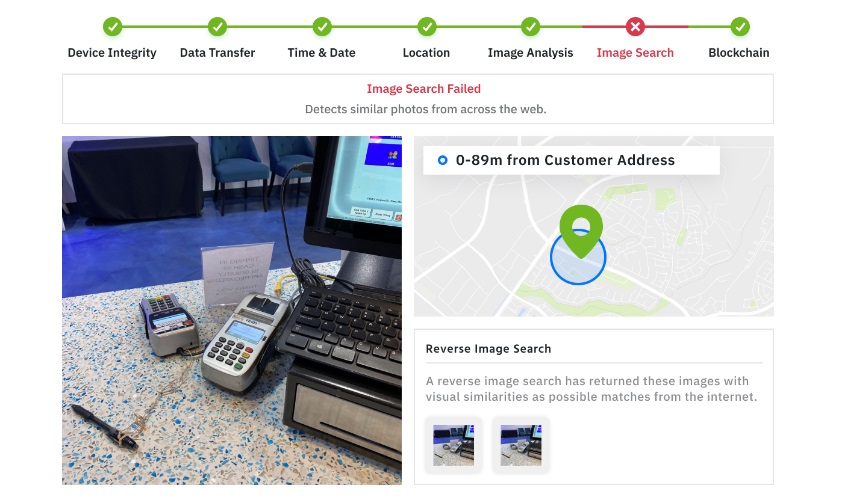
Companies offering technologies for preventing deep-fake
With the increase of damages from such forgery cases, more companies are now offering services that are similar to that of Team9, most notably Truepic and Serelay.
Truepic has shown remarkable growth since its foundation in 2015, now securing a total of 12 clients and partner companies. The company owns a technology that verifies fake photos/videos, which received authentication from the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) of the U.S. Department of Defense. It is collaborating with insurance companies and capital companies while also seeking joint businesses with dating app and e-commerce companies. What's notable about the technology of Truepic is that it can only verify photos and videos taken with the company's application (existing media from other sources cannot be uploaded). The taken photos are uploaded and stored only in the company's server in real time, and when the photos are shared externally, a unique watermark (with short URL) is embedded on them.
Serelay was established in 2017 under a business model that connects individuals with the media. The company received the Thames Valley Tech Awards in 2018 and Tech Nation's rising Star Awards in 2019, and is funded by Google News, Facebook, and European Space Agency. As for its key features and characteristics, the technology analyzes 300-500 elements of an image or video file by dividing the subject into 100 parts and marking areas suspicious of manipulation. It stores analysis and information on metadata sized less than 15kb in the photos, and uses them to verify whether the photos/GPS have been falsified or reused.
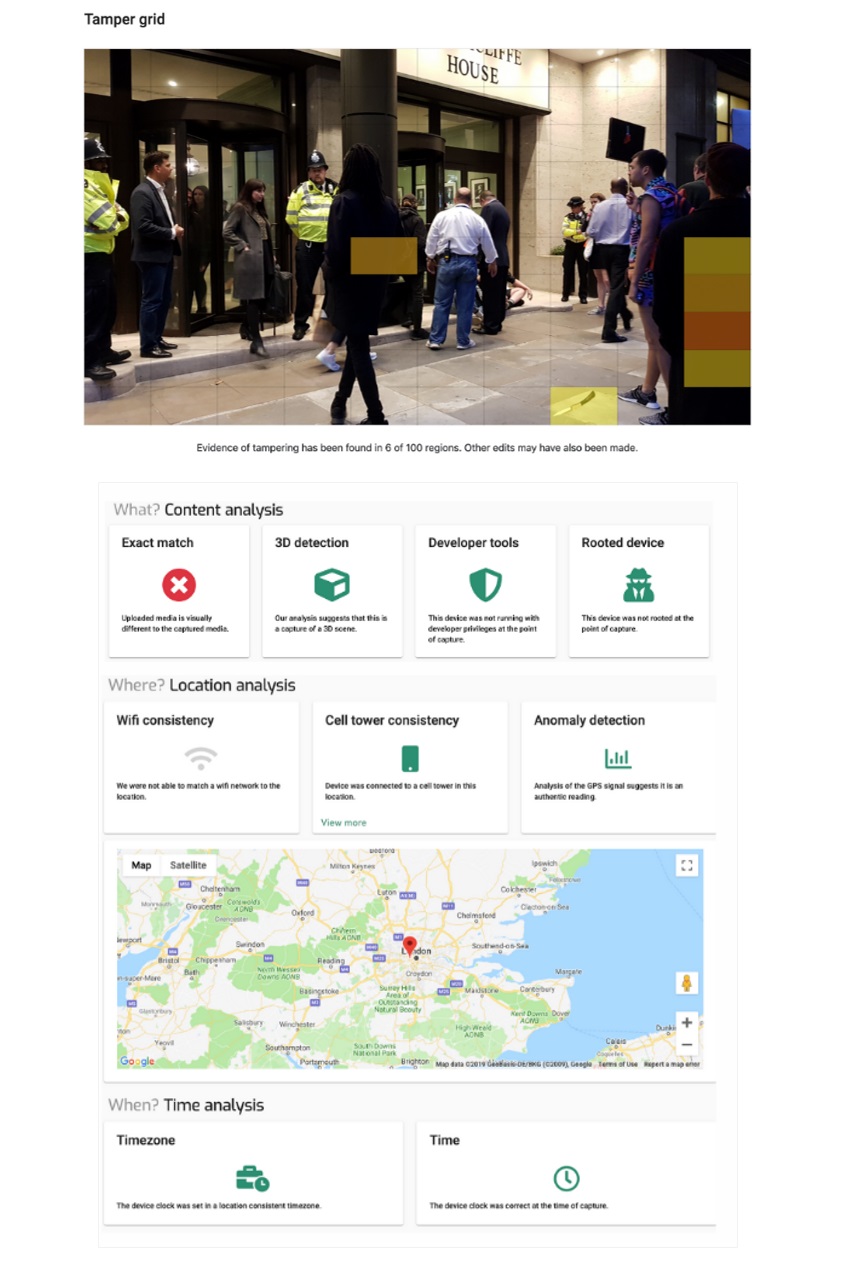
Even if the systems further develop, there will still be limitations in verifying forgery cases. But as more services that store original copies at the time of their shooting and prove their authenticity are widely offered in the market, it will be possible to prevent a large part of the damages resulting from forgery. Team9 plans to continuously carry out research and expand services on preventive technologies, so we ask for your wholehearted support for its future endeavors.
Read previous articles on deepfake:
+ Which One Is Real? Generating and Detecting Deepfakes
+ What Are Cheapfakes (Shallowfakes)?
+ What Is Proactive Media Forgery Prevention?
+ Is the Media You Are Watching "Real"?
+ Cheapfakes on the Rise in Zero Contact Environments
※ This article was written based on objective research outcomes and facts, which were available on the date of writing this article, but the article may not represent the views of the company.
