- This article is based on the content from the "Three Must-Know Digital Finance Trends and Utilization Strategies" and "Generative AI Utilization Strategies for Financial Institutions" sessions held during the "Samsung SDS Gen AI Day" seminar hosted by Samsung SDS for its financial clients in April 2024 -
The traditional financial industry's digital transformation began with the advent of cloud computing and the widespread adoption of smartphones, significantly altering not only the experience of financial services but also the daily lives of many people worldwide. Now in 2024, when you hear the term "digital finance," what keywords come to mind? Based on reports from global research firms and discussions held during business negotiations with IT and digital managers at financial institutions, the following keywords have been identified: GPT, LLM, Generative AI, Token Economy, STO, Open Pay, SuperApp, FinTech, Hyper-personalization, Embedded finance, Data Economy, and Cloud Platform.
 2024 Digital Finance Keywords (Source: Samsung SDS)
2024 Digital Finance Keywords (Source: Samsung SDS)
Among these various keywords, let's focus on three key trends to watch in 2024: △ Generative AI, △ Digital assets and the integration of tokens into the regulatory framework (STO, CBDC), and △ Changes and expansion in financial channels (SuperApp, Embedded Finance). We will take a closer look at the strategies companies should adopt to embrace the evolving market.
Generative AI
First, what does Generative AImean? Let's take a look at it based on a text analysis history of the domestic financial sector.
About 10 years ago, financial institutions in Korea widely adopted solutions that analyzed the frequency of meaningful text within sentences through morphological analysis of nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, particles, and other elements. To perform this analysis effectively, it was necessary to manually compile and input dictionaries of synonyms, plural forms, and other terms. Another approach used was the scenario rule-based chatbot solution, which defined specific answers to specific questions. Both solutions required extensive manual work and had significant limitations in sentence recognition and analysis. After a period of stagnation, financial institutions began to take an interest in the latter half of 2019 when Google published a paper on BERT* a transformer-based deep learning language model. Through vectorization technology, which converts text into numbers (embedding), models were trained using structured data as input. However, to achieve proper training, a large amount of data and costly infrastructure resources were required, and these efforts were limited to pilot projects due to a lack of BP (Best Practice) cases.
*Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (BERT) is a language model that uses only the encoder of a transformer to learn sentences bidirectionally. During the pre-training phase, it learns from a large dataset that isn't labeled, creating embeddings. In the fine-tuning phase, this embedding is used to learn from a smaller, labeled dataset to perform specific tasks.
In 2022, the emergence of OpenAI's ChatGPT sparked significant interest among financial institutions in generative AI and large language models (LLMs). ChatGPT's LLM, or GPT-n, is a deep learning language model based on transformers. It can eloquently respond to questions by learning from vast amounts of data, with its capabilities approaching the level of the human brain. Starting with the 117 million parameters of GPT-1.0, released in 2018, GPT-3.0 saw a significant increase to 175 billion parameters in 2020. Although the number of parameters for GPT-4.0, released in 2023, has not been disclosed, experts believe it exceeds one trillion. Deep learninguses a mathematical model known as an artificial neural network, inspired by how neurons in the human brain are connected. This machine learning algorithm learns complex patterns, and parameters such as weights and biases in neurons, play a crucial role in determining the performance of the model. [1] The human brain is composed of around 100 trillion synapses, which are comparable to neurons and parameters in deep learning. Although the number of parameters in LLMs has not yet reached the level of synapses in the human brain, rapid advancements suggest that they could soon achieve this level. Another important consideration is that, while the human brain is limited by its finite knowledge and experience, LLMs can learn from a vastly greater amount of information. Therefore, even without reaching the synapse level of the human brain, it's likely that LLMs surpassing human capabilities will emerge shortly.
 Text Analysis History in the Domestic Financial Sector (Source: Samsung SDS)
Text Analysis History in the Domestic Financial Sector (Source: Samsung SDS)
(1) Financial Sector Use Case
How can generative AI be used in financial operations? Since 2023, Samsung SDS has collected use cases not only from financial institutions but also across various industries, and after three months of analysis, secured over 200 actionable use cases ready for implementation. Some of these use cases are currently in the PoC stage, while others have moved beyond successful PoCs to actual implementation and operation.
In the financial sector, various use cases can be defined, such as Loan/Claims Assessment, Advertising/Brochure Generation, Portfolio Recommendation, Investment Management Information Generation, and AI Human Branch Teller. Let's look at two specific use cases in detail.
① Financial Interpretation Agent - Serving Foreign Customers at Bank Branches
As the number of foreign workers increases rapidly, financial transactions such as account openings are also on the rise. According to data released by the Ministry of the Interior and Safety, most foreign workers do not speak English and face difficulties communicating at the bank. To bridge this gap, employees often rely on translation programs, which makes communication challenging. Financial terminology is complex and often unfamiliar even to native speakers, making it difficult for foreign customers to understand standard translations.
If additional explanations are required, something as simple as opening a bank account can take up to two hours. In response, some banks have begun hiring professional interpreters in certain areas and are offering services by appointment, considering the associated costs. The “Financial Expert Interpreter Agent” uses generative AI to provide real-time interpretation in over 20 languages, including English, Chinese, and other in-demand languages like Cambodian, Mongolian, Vietnamese, and Filipino. It also reduces response time through interactive communication on mobile devices. What sets this apart from traditional translation tools is the application of Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) technology to the financial standard script. This technology converts the bank teller's questions into a standardized financial script before interpretation, helping to minimize the risk of miscommunication and reducing the chances of incomplete sales.
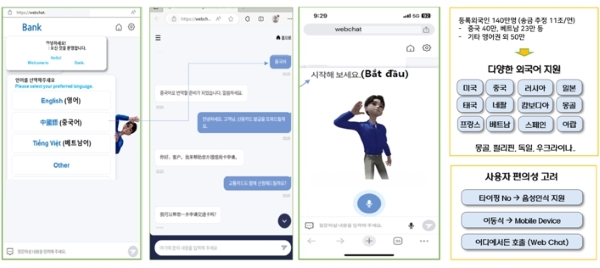 Financial Interpreter Agent UX (Source: Samsung SDS)
Financial Interpreter Agent UX (Source: Samsung SDS)
② Real-Time Investment Information Search Agent
Investment managers at securities firms or banks prepare daily for advisory sessions. They review overseas disclosure information, primarily focusing on large-cap stocks, posted on sites like the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission's (SEC) electronic filing site. For significant events, they translate and create content based on the information. This process typically takes at least 40 minutes to over an hour. Due to time constraints, small- and mid-cap stocks are often excluded, and critical information from real-time news, social media, or major reports from other firms may be omitted. Analysts need comprehensive analysis for all stocks. To support this, a Real-Time Investment Information Search Agent can be provided, which collects, translates, and summarizes disclosure information, news, and key reports from over 150 relevant sites, including Bloomberg, and generates reports. The content gathered from many websites can be refined and pre-processed to remove menus, ads, and other unnecessary elements. This allows investment managers to access up-to-date investment information on any stock anytime.
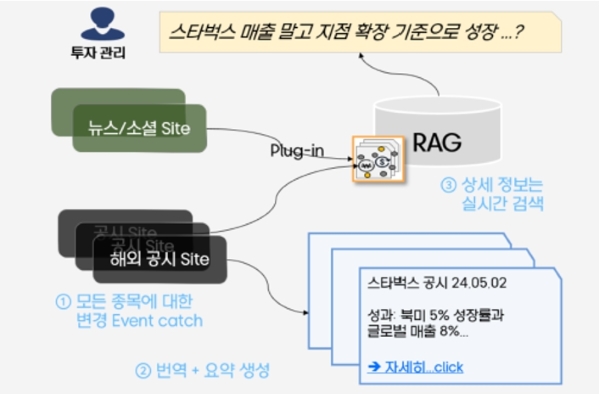 Real-time Investment Information Search Agent (Source: Samsung SDS)
Real-time Investment Information Search Agent (Source: Samsung SDS)
투자관리
-> plug-in -> RAG: 3 상세 정보는 실시간 검색 -> 스타벅스 매출 말고 지점 확장 기준으로 성장...?
-> 스타벅스 공시 24.05.02, 성과: 북미5% 성장률과 글로벌 매출 8%...
(2) Implementation Strategy Types
Many financial institutions are adopting generative AI, and the implementation strategies can be broadly categorized into three types.
The first approach is adopting a platform that can be used across the entire organization or group. Large financial institutions with strong vision and confidence in generative AI technology are either adopting a platform or building their own platforms. They gradually expand use cases and AI application areas by internalizing the technology. Although the initial costs may be high, this approach can reduce redundant investments for similar use case implementations in the long term.
The second approach is launching services by applying specific generative AI technology elements tailored to a preceding use case. While the initial cost may be lower compared to platform adoption, there is a significant risk of redundant investment, as generative AI services would need to be applied to each use case individually once the technology is established.
The third approach is conducting PoC or pilot projects, mainly pursued by small to medium-sized financial institutions. With high interest in generative AI, these institutions need to verify the technology but are cautious about the investment burden. They often wait to see industry trends before investing in best practices.
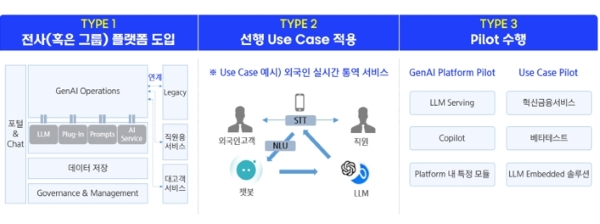 Types of Generative AI Adoption Strategies in the Domestic Financial Sector (Source: Samsung SDS)
Types of Generative AI Adoption Strategies in the Domestic Financial Sector (Source: Samsung SDS)
Given the rapid advancement of LLM models and the growing demand for generative AI, the platform-based approach, which requires higher initial costs but reduces redundant expenses and allows for quicker development and change management in the long term, is considered the most suitable of the three strategies. Samsung SDS also offers a generative AI service platform called FabriX, which supports everything from high-efficiency/high-security infrastructure to optimized LLM serving, integration between internal data/systems and external systems, user portals or chat services, and the development of legacy system copilots.
(3) Future Directions
Despite its rapid advancement due to its extensive learning capabilities, generative AI still has several limitations to consider when applying it to businesses.
In corporate settings, accuracy is just as important as stability. In the case of 'hallucination,' where the AI provides incorrect answers as if they are correct, there is a risk of complaints or lawsuits from financial institutions. Consequently, various technical efforts are being made to ensure accuracy.
For example, one approach is to 'fine-tune' with domain-specific data, or without fine-tuning the LLM model, to vectorize documents related to the domain and use Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) technology. In this case, queries are made to the vectorized DB, which then searches for relevant information and provides natural responses through integration with the LLM.
Additionally, ‘Prompt Optimization’ techniques can be used to frame questions more effectively so that the LLM provides better answers. Also, ‘Plug-in’ features can be leveraged to integrate and utilize domain-specific applications with the LLM. These advancements are significantly improving the accuracy of generative AI, thereby encouraging its adoption within enterprises.
Alongside these technical efforts, policy initiatives are also becoming increasingly important. Since AI is not perfect, safeguards are necessary for safe AI services. Companies are making various efforts to establish an AI governance framework to determine how to safely operate AI services and prevent the leakage of personal or corporate information through information protection measures.
Additionally, policies to promote AI are underway, following the relaxation of regulations for financial institutions. In March 2024, the Financial Services Commission launched the 'Financial Sector AI Council,' emphasizing the need for regulatory relaxation to promote generative AI in the financial sector and the importance of safe AI service utilization through AI governance.
The AI governance framework involves establishing AI ethical principles, which cover areas like privacy protection, respect for human rights, and corporate social responsibility. Based on these principles, it defines internal regulations, such as guidelines and related policies, and specifies the roles and responsibilities of departments involved with AI.
Furthermore, the AI governance framework includes AI governance implementation, which involves defining metrics at each stage of AI service planning, development, verification, and operations to assess risk levels and monitor compliance. To manage this overall governance framework, it is essential to have AI governance technology (systems), such as AI platforms, system toolkits, and AI dashboards. Through the AI governance system, financial institutions can monitor the overall status of AI systems/services in operation and the risk levels of each system/service. For instance, for an AI service like 'general loan credit rating calculation,' the system can manage indicators, such as performance, whether it remains under human control, respects customer rights, protects personal/sensitive information, and is explainable.
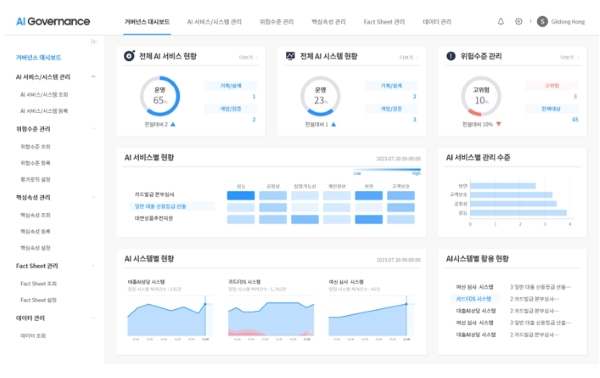 AI Governance - Management and Monitoring Example (Source: Samsung SDS)
AI Governance - Management and Monitoring Example (Source: Samsung SDS)
Token Integration into the Regulatory Framework
(1) STO
Security Token Offering (STO) refers to the issuance of blockchain-based digital assets) classified as securities. Recently, there has been significant interest in STOs, particularly among securities firms. Central public institutions related to domestic securities trading are conducting "consultations for requirement specification" to standardize STOs. The STO domain presents an opportunity to securitize and trade new assets that were not previously traded as securities. This includes physical assets like artwork and high-value items, as well as intellectual property, such as movie and music copyrights, which can be securitized and circulated in the market. A notable example is ) fractional investment, which is closely related to STOs). Fractional investment involves investing in a portion of an asset. For instance, MUSICOW allows multiple people to invest in music copyrights, TESSA focuses on art, Bankcow offers fractional investment in Hanwoo cattle, and Treasurer provides a platform for investing in luxury goods. As more people engage in fractional investments, the blockchain-based STO market is poised to offer significant opportunities for this new form of securities trading.
In June 2023, the Act on the Protection of Digital Asset Users was enacted and is set to be implemented in July 2024. This law aims to strengthen regulations, but conversely, digital asset trading could become highly active by ensuring compliance with these regulations. Centered around securities firms, efforts are underway to establish STO platforms that provide ST issuance, ST distribution management, blockchain-based distributed ledger management, and interfaces linking external institutions. These platforms will lay the foundation for the digital asset ecosystem and secure leading technologies to respond to market changes.
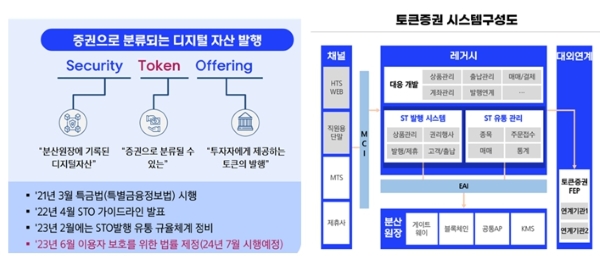 STO Definition and Platform Configuration Example (Source: Samsung SDS)
STO Definition and Platform Configuration Example (Source: Samsung SDS)
증권으로 분류되는 디지털 자산 발행
- Security
- 분산원장에 기록된 디지털자산
- Token
- 증권으로 분류될 수 있는
- Offering
- 투자자에게 제공하는 토큰의 발행
- 21년 3월 특금법(특별금융정보법) 시행
- 22년 4월 STO 가이드라인 발표
- 23년 2월에는 STO발행 유통 규율체계 정비
- 23년 6월 이용자 보호를 위한 법률 제정(24년 7월 시행예정)
토큰증권 시스템구정도 이미지
(2) CBDC
CBDC refers to a digital currency issued by a central bank, which is different from traditional currency in the way it is issued. From 2021 to 2023, the number of countries and currencies that have either launched, are piloting, or are developing blockchain-based CBDCs has continued to grow. In South Korea, the Bank of Korea established a pilot CBDC system in 2021, implementing the basic issuance, distribution, and redemption processes. In 2022, they conducted tests linking the CBDC pilot system with financial institutions. In 2024, a real transaction test using digital vouchers is planned for 100,000 participants. Digital vouchers apply digital currencies to existing voucher systems, which have been prone to fraudulent or illegal activities. Therefore, applying a blockchain-based digital currency to these vouchers is considered the most suitable approach to enhance transparency. If the performance and effectiveness of the digital voucher market are confirmed, the use of digital currencies could expand significantly.
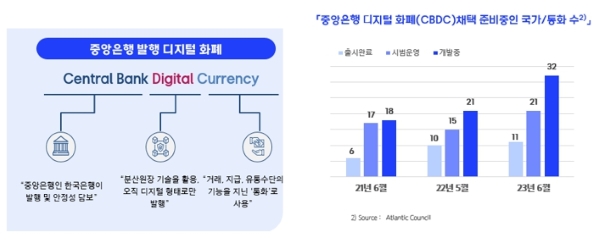 CBDC Definition and Central Bank Digital Currency Readiness (Source: Samsung SDS)
CBDC Definition and Central Bank Digital Currency Readiness (Source: Samsung SDS)
중앙은행 발행 디지털 화폐
- Central Bank
- 중앙은행인 한국은행이 발행 및 안정성 담보
- Digital
- 분산원장 기술을 활용 오직 디지털 형태로만 발행
- Currency
- 거래, 지급, 유통수단의 기능을 지닌 통화로 사용
- 21년 6월
- 출시완료:6 시범운영:17 개발중:18
- 22년 5월
- 출시완료:10 시범운영:15 개발중:21
- 23년 6월
- 출시완료:11 시범운영:21 개발중:32
The Evolution and Expansion of Financial Channels
(1) SuperApp (Market and Platform)/MiniApp
Since the COVID-19 pandemic, the expansion of contactless financial channels has accelerated significantly. As part of this trend, major financial institutions are preparing to launch and upgrade SuperApps. Just as portal websites were central to the rapid growth of the Internet, SuperApps are at the heart of the new paradigm in the mobile era.
A SuperApp provides various lifestyle services within a single, integrated platform, offering a seamless user interface. This approach is designed to capture customers' attention by providing convenient access to high-quality content and diverse services, ultimately contributing to strong customer retention, known as "lock-in." [2] According to "Data.ai," a site that analyzes app usage statistics, from January to March 2024, the app with the highest average daily usage was YouTube. In the financial SuperApp category, Toss ranked 56th overall (and first among financial SuperApps). Other financial SuperApps ranked outside the Top 100. Unlike other financial platforms, Toss lacks an offline alternative channel and focuses on providing various short-term events and payment services. Toss has created a highly convenient user-friendly interface by emphasizing the user experience through the operation of agile teams specialized in channel development. This approach, offering financial services that are simple and easy to use, has garnered significant support and empathy from the MZ generation (Millennials and Generation Z).
China's "WeChat," developed by Tencent, is a leading example of an international SuperApp, integrating lifestyle services like online shopping, virtual wallets, and payment services, all centered around its messaging platform. One of the key technologies behind WeChat's success is the MiniApp. As of the first quarter of 2022, WeChat offered over 3.5 million MiniApps, allowing users to access services directly within WeChat without downloading separate applications. Similarly, Toss's SuperApp offers an in-app service for train ticket booking, eliminating users needing to install a separate KTX application. In 2020, Apple introduced App Clips, a MiniApp that allows users to access certain app features without fully installing the app. This lightweight version of an app can be quickly accessed via QR codes, NFC tags, or app links in messages, enabling users to perform tasks like ordering food, renting bikes, or setting up electronics swiftly and conveniently. [3] Despite offering many services, WeChat's MiniApps provides a simplified UI/UX, making them remarkably easy for customers to use. This approach is a crucial technical element that financial institutions looking to develop their SuperApp platforms should consider adopting.
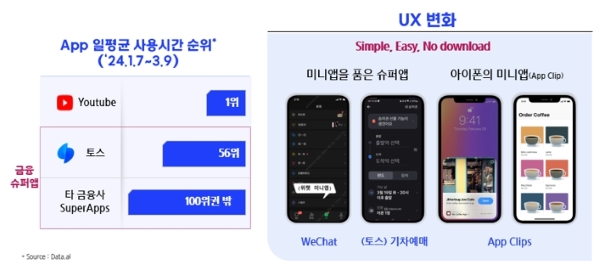 SuperApp UX Changes (Source: Samsung SDS)
SuperApp UX Changes (Source: Samsung SDS)
(2) Embedded Finance
Embedded Finance refers to the integration of fintech functionalities into the platforms of non-financial companies, going beyond merely brokering or reselling financial products of financial institutions. A notable example is Naver Financial, a subsidiary of Naver, partnering with Mirae Asset Capital to offer credit loan products to merchants on Naver's Smart Store platform. Although the term has not been around for long, its application is widespread.[4]
One aspect of Embedded Finance is the concept of 'agency banking.' The Financial Services Commission is considering the introduction of agency banking, where non-bank channels, such as post offices, convenience stores, and insurance agencies, could handle simple banking tasks.[5] As the reduction of physical bank branches accelerated post-COVID, agency banking could enhance financial accessibility for digitally vulnerable groups while allowing internet-only banks to easily establish offline channels. However, challenges remain regarding how to enforce control, manage risks, and assign responsibilities. However, advanced countries, such as the United States, Japan, and Australia, have already activated and operate agency banking systems tailored to their specific national context. Therefore, it is expected that active consideration of this model will continue.
Another example of Embedded Finance is In-Car Payment systems. In-Car Payment allows drivers to use various payment methods for services at convenience stores, cafes, gas stations, and parking lots by pre-ordering and paying from within their car using a registered card. In South Korea, companies like Hyundai, Kia, and Renault Samsung Motors are offering In-Car Payment services, with the number of affiliated merchants continually expanding from around 4,000 as of the end of 2023.[6] Initially focused on online shopping, embedded payment services are expanding beyond web-based payments including Danggeun Pay and Coupang Pay to include offline channels such as automotive payment systems.
 Expansion of Embedded Finance Channels (Source: Samsung SDS)
Expansion of Embedded Finance Channels (Source: Samsung SDS)
| 구분 | 일본 | 미국 | 호주 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 유형 | 은행대리점 | 제휴, 위탁 | 제휴, 위탁 |
| 수행자 | 금융기관, 법인, 개인 | 제한 없음 | 우체국 |
| 업무 | 은행의 본질업무(계좌 개설, 대출, 외환)등 | 위탁 받은 업무만 스행 가능 | 계좌입금, 현금인출, 청구서 지불 |
Afterword
The development of mobile banking and the impact of COVID-19 have firmly established contactless and digital finance as the norm. The emergence of fintech, a new form of financial service combining IT and mobile technology, has allowed all financial transactions to be handled easily and conveniently via smartphones, transcending time and space while also offering new value to customers. The financial market is witnessing a major digital transformation, driven by technological innovations such as artificial intelligence, big data, blockchain, and cloud computing. Rapid changes in trends, including the expansion of generative AI, digital assets, and financial channels, are becoming increasingly evident.
Generative AI, based on LLMs growing faster than ever over the past decade, requires the courage to entrust tasks to AI and make bold investments. It is essential to identify the most prioritized and efficiency-enhancing tasks to uncover use cases, and to consider or promote the adoption of a generative AI service platform-based approach, such as FabriX from Samsung SDS, which can support various use cases across the board. Also, digital asset tokens emerging as a new type of asset should be researched and developed as new revenue stream. Securing the foundation for a digital asset ecosystem through infrastructure built on blockchain is crucial. Lastly, SuperApps, which allow customers to access various financial and lifestyle services within a single app without needing to use multiple apps, require a strategy focused on easy access to services through user-friendly design and interfaces, along with a proactive technical review of mini-app integration for partner services, which is considered the core of such apps.
References
[1] https://blog.naver.com/cdogcapj86/223458640668
[2] https://terms.naver.com/entry.naver?docId=6685239&cid=42107&categoryId=42107
[3] https://www.ciokorea.com/column/270825
[4] https://blog.naver.com/bainseoulmarketing/222954202169
[5] https://alphabiz.co.kr/news/view/1065603010067489
[6] https://www.donga.com/news/article/all/20210701/107739927/1
- #FinancialTrends
- #DigitalFinance
- #EmbeddedFinance
- #AI
- #AIPlatform
- #AIGovernance
- #GenerativeAI
- #GenAI
- #LLM
- #LargeLanguageModel
- #ChatGPT
- #DigitalAsset
- #Token
- #STO
- #SecurityTokenOffering
- #CBDC
- #CentralBankDigitalCurrency
- #SuperApp
- #MiniApp
- #InCarPayment
- #UseCase
- #FabriX

Strategic Marketing Team at Samsung SDS
Had been in charge of digital transformation in samsungsds.com, solution page planning/operation, based on her work experiences in IT trend analysis, process innovation, and consulting business strategy, and is now in charge of content planning and marketing through trend/solution analysis for each main business sector of SDS.
