ChatGPT, Generative AI!
Everyone has heard these terms at least once. With a rapid AI advancement, however, a new question arises.
“What’s next?”
“How far will AI evolve?”
At the center of this question, there is a concept that has recently been in the spotlight — AI agents.
Even a few years ago, AI agents just began to gain attention through web search and initial cases. This year, however, the most notable keyword of CES 2025 was definitely AI agents.
Why Are AI Agents Attracting Attention?
AI agents are intelligent software systems that operate independently without human intervention and recognize and learn environments to achieve goals and resolve problems. They seem like future technologies but the agents have been creating a new paradigm as used in daily and business tasks.
Why is there so much attention to AI agents now?
This transformation began with the COVID-19 pandemic. The pandemic forced companies around the world to quickly adapt to remote work and digital transformation. To maintain productivity and competitiveness, the companies had to introduce intelligence systems beyond a simple automation. In this transformation, the need of AI agents arose since they can understand and learn environments and support decision-making. After the pandemic, AI agents have been used as a tool to bring fundamental changes to traditional ways of working. AI agents have now become a necessity across industries by creating new values through business automation, customized services, and real-time decision-making support.
In particular, the emergence of generative AI accelerated the advancement of AI agents. Generative AI, such as OpenAI’s ChatGPT, supports complex decision-making beyond creating communication, enabling users to immediately respond to business needs. Generative AI has transformed enterprises’ productivity and efficiency and raised potential power of AI agents.
Ultimately, AI agents are a technology that has created powerful synergies in the midst of technological evolution and economic necessity. This will not end as just a trend. AI agents will firmly establish themselves as a core driving force of future business and industry.
How Did AI Agents Evolve?
How did AI agents get to where they are now? The evolution of AI agents is more than just a technological evolution; they were advanced by responding to users and changes across industries.
At an early stage, AI systems worked based on specifically defined rules. The systems mainly focused on resolving simple problems such as a FAQs chatbot and a reservation system. However, these systems had limitations on adapting to environmental changes and handling unstructured data. With the advent of generative AI, however, AI agents have gone beyond simple data processing to understand and learn the context like humans, gaining abilities to extract patterns from a large volume of data and address more complex issues.
The emergence of multimodal AI allowed AI agents to support a unified data processing, such as text, voice, and image, driving innovations. In ecommerce industry, for instance, AI agents analyze customers’ search history and purchase patterns, providing customized recommendations. In healthcare, AI agents comprehensively analyze patients’ medical records and real-time data to suggest personalized diagnosis and treatment plans.
Now, AI agents have gone beyond users’ assistants to become autonomous systems that define and solve problems by themselves. They show differentiated characteristics from conventional technologies such as chatbots and virtual assistants.
- Differences from chatbots: AI agents understand the context of communication and suggest tailored solutions while chatbots just answer questions and provide static information.
- Differences from virtual assistants: AI agents help complex decision-making through comprehensive data analysis while virtual assistants just handle alarm setup and simple tasks.
AI agent will evolve into more integrated and adaptive forms. As a single platform converged with generative AI and multimodal AI, AI agents will transform into systems that provide various features and flexibly adapt to changing needs of users.
Why Do AI Agents Matter?
AI agents are no longer a story of a very distant future. This technology has already been embedded deeply in our daily lives, both in business and in our personal lives, becoming a pivot that maximizes productivity and efficiency and drives new innovations. Why are AI agents considered an important technology? Let’s look at their importance from the following three perspectives.
Innovate Business Automation
Beyond automation of repetitive tasks, AI agents have been changing a work paradigm by supporting complex data analysis and real-time decision-making. For instance, financial institutions analyze thousands of transactions in real time using AI agents to detect fraudulent transactions, building reliable security systems. With AI agents, employees can focus on more strategic and creative tasks rather than simple data processing.
Advance personalized customer experience
Through in-depth analysis of customer data, AI agents provide personalized services tailored to individual’s preferences and behavior patterns. For ecommerce platforms, AI agents analyze customers’ behavior patterns and provide personalized recommendations, improving customer satisfaction and increasing sales. A retail company saw an increase in purchase conversion rate by 20% after AI agent introduction as well as significant improvement of customer loyalty.
Accelerate data-based decision-making
In today’s business landscape, data gives a greater upper hand to enterprises. AI agents analyze a vast amount of data and utilize prediction models to help optimal decision-making. With AI agents, manufacturers optimize inventory management and alleviate bottlenecks of logistics systems, significantly improving operational efficiency. In addition, they promptly respond to market changes through data-based insight to maintain competitiveness.
In this sense, AI agents not only represent technological advancement but will also become essential tools to fundamentally transform the way we work and the industrial structure.
AI Agent Architecture
According to World Economic Forum (WEF), AI agents adapt to user requirements and environmental changes and work autonomously based on architecture composed of Environment, Sensors, Learning, Control Centre and Effectors. By combining with Large Language Models (LLMs), copilot and automation, AI agents become more intelligent with greater executing ability.
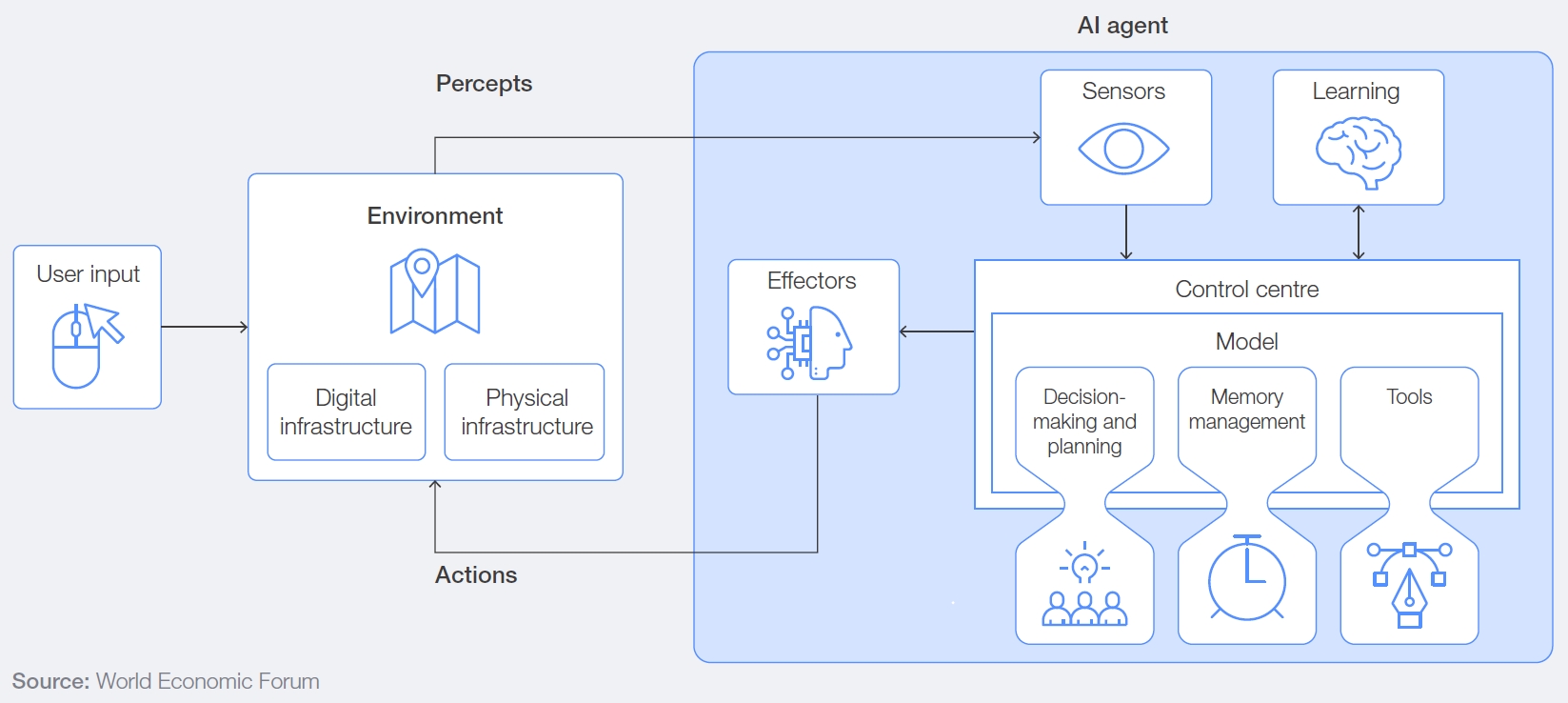 Key Components of Advanced AI Agents (Source: World Economic Forum)
Key Components of Advanced AI Agents (Source: World Economic Forum)
AI agent
Sensors → Control centre
Learning ←→ Control centre
Control centre
Model
- Decision-making and planning
- Memory management
- Tools
Control centre → Effectors
Effectors → Actions → Enviroment
Environment
Digital infrastrcture
Physical infrastructure
User input → Environment
Enviroment → Percepts
Environment: Digital and Physical Infrastructures
Environment module is divided into digital infrastructure where AI agents work (cloud systems, networks, etc.) and physical infrastructure (IoT devices, robotics, etc.). LLMs, copilot and automation interact together in the environment to optimize outputs.
Sensors: Collect and Understand Data
Sensors module is the first step for AI agents to collect data in digital and physical environments and LLMs understand the data and interpret the context. Based on these data, LLMs comprehensively process multimodal data including text, voice, and images and passes the output to the next step. In other words, this component recognizes the environment through user input data, digital logs, and IoT sensors, and transfers this data to Control Centre in an analyzable form.
Learning: Continuously Improve Performance
Learning module improves performance through data received from Sensors and its past memory. With this, AI agents are no longer static, adapt to changing environments, and show more sophisticated behaviors.
Control Centre: Make Decisions and Planning
Control Centre plays a role as brain of AI agents and processes data and makes decisions. In this module, LLMs, copilot and automation take their unique responsibilities and work together.
- Large Language Models (LLMs): Analyze data and design optimal strategies to achieve goals.
- Copilot: Support users to perform tasks intuitively based on LLM-created plans and data.
- Automation: Automate business processes from simple tasks to complex processes using technologies including RPA.
Effectors: Execute Planned Actions
Effectors executes actions planned by Control Centre in the digital and physical environments.
With this architecture, AI agents actively adapt to user requirements and environmental changes, evolving as intelligence systems that make advanced decisions.
AI Agent Solutions Suggested by Samsung SDS
A solution, more than just technology, is required to maximize potential power of AI agents and secure competitiveness in a changing digital environment. Samsung SDS offers various solutions such as FabriX, Brity Copilot, and Brity Automation, covering all processes from AI agent design, execution, and management to optimization.
FabriX: Core Infrastructure of AI Agents
FabriX is a generative AI platform for enterprise that integrate and utilize enterprise data. It provides an optimal environment for AI agents to learn and execute. In particular, FabriX can understand complex languages and shows a greater ability to generate outputs based on Samsung Large Language Model (Samsung LLM) developed by Samsung Research. In addition, FabriX designs agents optimized in certain tasks and environments by combing various AI models.
Unique Features of FabriX:
- Designs and distribute enterprise-tailored AI agents using Agent Studio
- Shares knowledge assets and collaborate via Prompt Studio and Prompt Library
- Analyzes data in real-time by seamlessly integrating with key systems including ERP and CRM
Beyond a technology platform, FabriX is a robust foundation for enterprises to create new values through AI agents.
Brity Copilot: Digital Assistance Driven by AI
As a digital assistant, Brity Copilot enables users to enjoy generative AI services across mail, messenger, and meeting whenever wherever. With Brity Copilot handling most of the everyday tasks, such as real-time captions and translation during meetings, Q&A on meeting content, creating meeting minutes, summarizing chat on messenger, and writing emails, users can focus on more strategic and creative work.
Key Features of Brity Copilot
- Supports real-time captions and meeting summary with high voice recognition rate (higher than 94% for Korean)
- Automatically blocks sending data using keyword and message pattern analysis when sensitive internal information or source codes are included
- Provides integrated search by linking with internal systems
Brity Copilot provides enterprise-tailored generative AI services that transform the way you work.
Brity Automation: Realizing True Hyper-Automation
Brity Automation supports AI agents to handle all complex work processes simply beyond RPA. By integrating various AI technologies such as machine learning, natural language processing, OCR, and others, it enables efficient automation of repetitive and time-consuming tasks.
Key Features of Brity Automation
- Supports end-to-end automation from simple tasks to complex workflows
- Expands range of implementation of automation using 660 types of automation libraries
- Easier automation supported by generative AI
- Enables decision-making based on collaboration with humans through Human-in-the-Loop (HITL)
With generative AI-powered Copilot features, Brity Automation enables chat-based task design and execution and provides users with simple notifications, progress approval, and work details, enabling automation from start to finish.
Summary
AI agent is not a technology of the future, but a technology that is driving innovation today. AI agents set new standards across industries from business automation, customized services to data-driven decision-making.
Companies should concentrate on strategically utilizing AI agents to gain a competitive edge. As a strategic partner, Samsung SDS provides an integrated and flexible support system that maximizes the capabilities of AI agents while enhancing organizations’ productivity and efficiency.
References
[1] Navigating the AI Frontier: A Primer on the Evolution and Impact of AI Agents:
https://www.weforum.org/publications/navigating-the-ai-frontier-a-primer-on-the-evolution-and-impact-of-ai-agents/
[2] Levels of AI Agents: from Rules to Large Language Models:
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2405.06643
[3] Intelligent Agents: Theory and Practice:
https://www.cs.cmu.edu/~motionplanning/papers/sbp_papers/integrated1/woodridge_intelligent_agents.pdf
[4] AI Agents from Copilots to Coworkers: Historical Context, Challenges, Limitations, Implications, and Practical Guidelines:
https://www.preprints.org/frontend/manuscript/7f860946f8f6008f5ef187a10a1c07d3/download_pub
[5] AI Agents That Matter:
https://arxiv.org/abs/2407.01502
[6] The Rise of AI Agents: Unleashing Productivity and Innovation:
https://www.oracle.com/a/ocom/docs/applications/the-rise-of-ai-agents-unleashing-productivity-and-innovation.pdf
[7] Prompting for action: How AI agents are reshaping the future of work:
https://www2.deloitte.com/content/dam/Deloitte/us/Documents/consulting/us-ai-institute-generative-ai-agents-multiagent-systems.pdf
[8] What Are AI Agents?:
https://www.ibm.com/think/topics/ai-agents
[9] CES:
https://www.ces.tech/
[10] FabriX:
https://www.samsungsds.com/kr/ai-fabrix/fabrix.html
[11] Brity Copilot:
https://www.samsungsds.com/kr/copilot/brity-copilot.html
[12] Brity Automation:
https://www.samsungsds.com/kr/ai-automation/brity-automation.html
▶ This content is protected by the Copyright Act and is owned by the author.
▶ Secondary processing and commercial use of the content without the author’s permission is prohibited.

Strategic Marketing Office, Samsung SDS
Corporate Strategy & Business Development, and Customer Success Lead
