IDC survey suggested that volumes of worldwide data are doubling every two years, and storage volumes handled by companies are increasing by an annual average of more than 50%, resulting in exponential increase of the cost of data management.
Is there way to reduce ever-growing costs of managing data? Let’s examine Information Lifecycle Management(ILM) concepts and implementation technologies reducing operational costs with efficient data management, along with Samsung SDS’s ILM solution.
What is ILM?
Not all the data is valuable in the incredible volume of data. They eventually become outdated or no longer needed. The frequency of their use drops dramatically after one year depending on the data type.
The question “Is it necessary to store all the data in the same way?” was catalyst for developing ILM.
Data Data also live and die on the product lifecycle. When data is first created it is used frequently, and then gradually the use frequency declines.
ILM is the management of the data to lower operation costs by optimizing the retention period of data in accordance with their lifecycle.
Storage Networking Industry Association(SNIA) detailed its vision of ILM, stating ‘ILM is comprised of the policies, processes, practices, and tools used to align the business value of information with the most appropriate and cost-effective IT infrastructure from the time information is conceived through its final disposition.’ ILM encompasses technology that defines and implements efficient management of data.
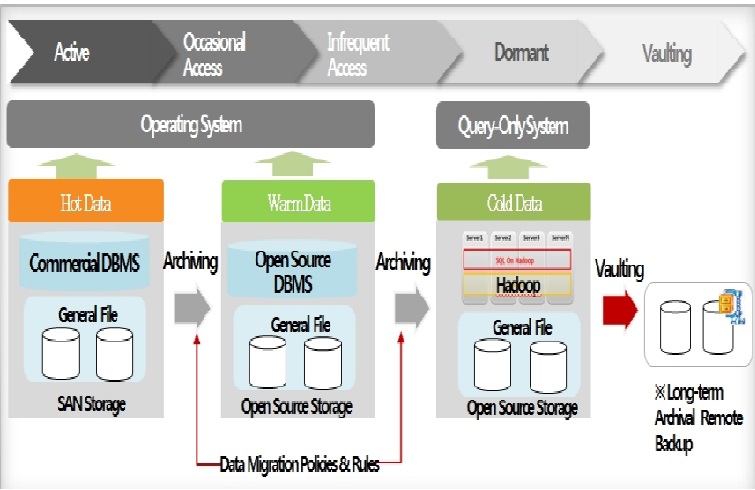
 Change in Management Method Based on Data Life Cycle
Change in Management Method Based on Data Life Cycle
ILM drew a lot of attention from the IT industry in the mid-2000s and has been in the spotlight again recently. With the advent of new services such as big data analytics, the need to preserve large amounts of data is constantly growing.
In addition, the development of open source distributed storage technology that uses the general-purpose hard disk of x86 server as storage enables companies to easily configure low-cost storage without storage vendors, hus reducing big data operation costs.
Tougher compliance requirements along with the increase in the amount of data are emphasizing the importance of ILM. Even though some of the data are no longer considered to be valuable, there are exceptions that require long-term retention periods, such as the data referenced primarily in dealing with lawsuits and disputes, with mandatory retention periods set by law.
In the United States, the Sarbanes-Oxley Act(U.S. federal laws pertaining to accounting firm audit) and the Health Insurance Portability & Accountability Act (HIPAA) require long-term retention of data, for instance, HIPAA stipulates that it is mandatory to retain pediatric patients’ medical information for more than 21 years.
Finance companies in Korea also store and manage financial transactions in accordance with the guidelines of the Financial Supervisory Service, and likewise domestic manufacturers retain manufacturing information for 5 to 20 years in contingency for international patent disputes.
ILM Technology
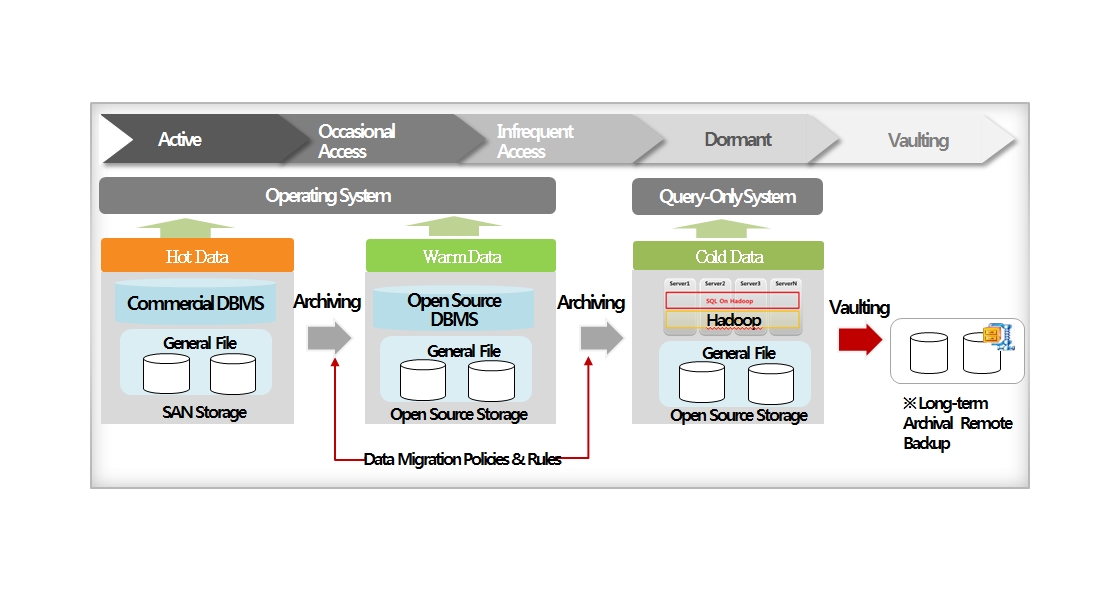
ILM is one of the technical components of enterprise data management architecture.
The most important technology for implementing ILM is archiving management that sorts out low value data from high-value operating storage data and migrate them to low cost storage.
 Data Management Architecture
Data Management Architecture
Data archives are often confused with data backups which refer to the copying of snapshots of operational data so they may be used to restore the original after a data loss event.
In contrast, archiving is the process of moving data that is no longer actively used to a separate storage device for regulatory yet also enables immediate utilization of older data whenever necessary. The data archives serve as a way of reducing primary storage consumption and hence improving efficiency of operating system, which can’t be achieved by backups.
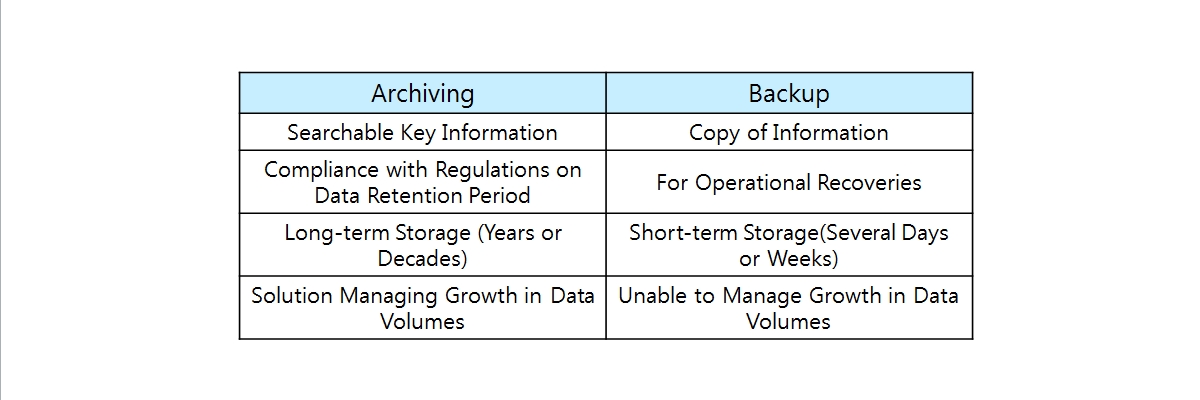 Archiving vs. Backup
Archiving vs. Backup
ILM Solution Types
Manually migrating large volumes of data from primary storage to low-cost archival storage is a difficult undertaking. An automated solution is required to manage the entire migration procedure, encompassing definition of data management policies, job/schedule definition, migration as well as result monitoring.
There are a wide variety of commercial solutions on the market that automate and implement ILM concept.
As shown in the diagram below, ILM solutions are categorized into three main types, and each has its own pros and cons, so it is vital to select the product suitable for each operation.
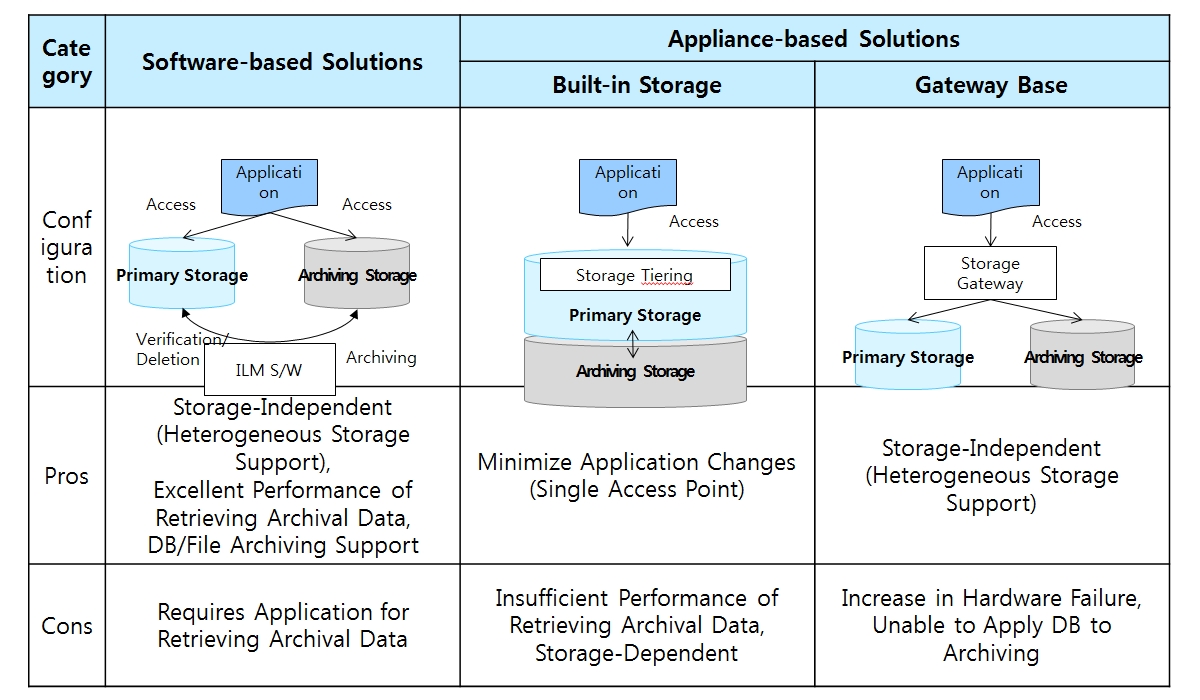 ILM Solution Types
ILM Solution Types
ILM solutions provided by storage vendors are dominated by ‘built-in storage’.
The storage itself has a tiering function, allowing the data to be divided into high performance and low performance storage according to a set of rules. An application has a single access point to primary storage and doesn’t need to recognize archiving storage separately.
On the other hand, when retrieving archived data, the data is restored to the primary storage, resulting in degraded query performance. The downside is that storage products available are also limited.
The recent emergence of a number of open source distributed storage solutions have facilitated technology development of configuring mass storage at low cost using general-purpose hard disks of x86 server. Currently, there is a product on the market comprising 600TB of storage with just one x86 server and further developments are expected (10TB HDD 56 Slots (60 Slots when expanded)). Reflecting these technological advances, ILM products are emerging that are not dependent on specific storage but are ‘software-based’ and ‘gateway-based’ supporting universal storage.
ILM Introduction Process
Data handled by companies consist of a variety of types such as ERP (SAP, etc.) DB, Non-ERP DB and file. Establishing a consistent data management policy from a company-wide perspective is a prerequisite to adopt ILM.
Once the data management policy of the entire enterprise is determined, it is necessary to define detailed migration targets and standards by analyzing the characteristics of the management target data (life cycle-based value importance, frequency of use, data type – basis info., temporary info., etc.) by system.
Migration criteria, as well as operation criteria, such as the migration policy change criteria and the data deletion policy are defined and job/schedule are designed to execute these criteria. The execution of migration is confirmed through the initial data migration and verification, and then its full-scale application starts.
Features of Samsung SDS ILM Solution
Isn’t ILM a solution provided by storage vendors? How come Samsung SDS, a service provider, can provide ILM solution?
Now it’s time to stop depending on storage vendors to configure archiving storage with the advances in open source technology. Based off open source DB and distributed storage technologies, Samsung SDS is securing technologies to implement ILM that is independent from storage.
Samsung SDS collects requirements from the field, defines job/schedule on the basis of data management policy, and secures SDS ILM solution that automatically migrates operational data to low-cost storage to apply it on site.
Software-based ILM solution which supports inexpensive storage consisting of general-purpose hard disk, not directly involved in data access of application is adopted.
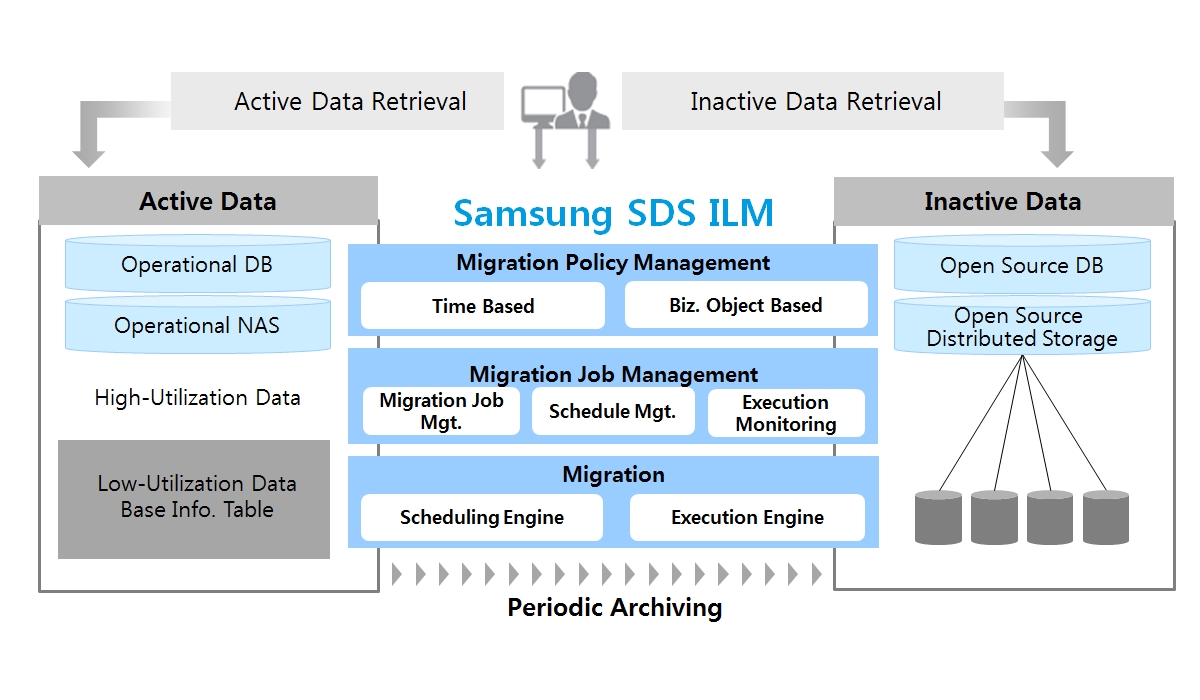 ILM Feature Configuration
ILM Feature Configuration
Main features of Samsung SDS ILM are as follows.
1) Business rule based migration policy management
Provides various policy definition features such as time based policy (based on data generation time) and business object based policy (data classification related to business rules, e.g. long-term inpatient data)
2) Visual Archiving Process Design
Provides intuitive migration workflow design using graph notation
3) Job/Schedule management and automatic migration
Provides the feature that automatically generates the migration program and executes the migration process
The most significant feature of SDS ILM is that it uses open source DB and open source distributed storage to reduce storage cost, unlike commercial solutions that use specific commercial products for archiving storage configuration.
It facilitates data migration from Oracle to PAS/Ceph for DB archiving, from NAS to GlusterFS and from NAS to low-price NAS for file archiving. With storage-independent migration technology, storage of the migration target is scalable.
Note) PAS: Postgres Advanced Server is based on the open-source database PostgreSQL and has also developed database compatibility for Oracle
&nbs;p Ceph : x86-based open source distributed storage software with scale-out architecture
GlusterFS : open source distributed storage software applicable to scalable network file system development
ILM Introduction Effect
Samsung SDS ILM reduces IT expenses and improve operational performance.
As the amount of data increases, operational data retrieval performance of the system using DB decreases, and backup and recovery takes longer, resulting in reduced operational efficiency. Separating the data deemed to be less valuable from operational storage can reduce data volumes, thereby improving query performance and efficiency of operating system. Utilizing open-source DB enables reduction in DB license cost as well.
The result of analyzing the effect of applying Samsung SDS ILM to the site is shown in the following chart.
It showed that replacing the existing high-priced hardware and software with the low-cost storage will cut expenses by more than 30%, compared to the cost of increasing them. Reduced operational data also improved operating system query performance, backup, and recovery efficiency by over 30%.
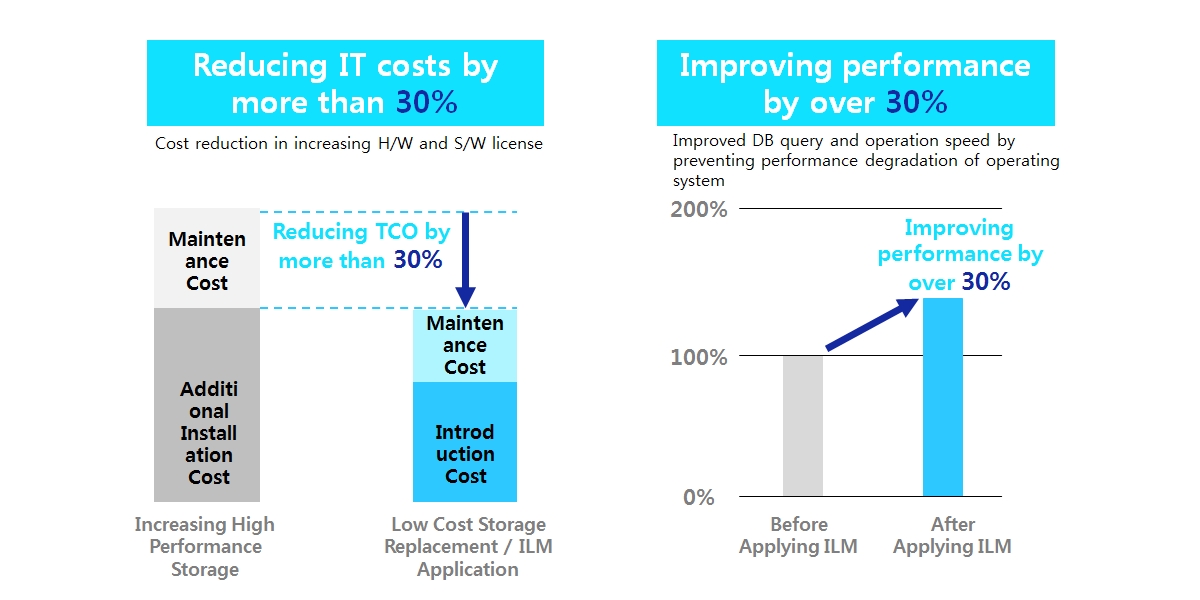 Samsung SDS ILM Introduction Effect
Samsung SDS ILM Introduction Effect
Improvement of Samsung SDS ILM
Introduction of ILM is essential for companies handling data to efficiently manage ever-growing mass of data.
For instance, whenever a cellphone manufacturer releases a new model, its data use has more than doubled that of the previous version.
Efficient data management, especially preserving and handling large volumes of data, from analytical data to operational log data, is urgently needed. To address this challenge, Samsung SDS secures ILM solution and applies it to the field, while developing technology and accumulating operational know-how.
Samsung SDS ILM has three main features to be added in the future.
First, archiving in public/private cloud storage will be available soon.
We are preparing for migration feature to Samsung SDS’s cloud storage service, Samsung owned File System (SoFS).
We will also support data migration to public cloud storage to support customers using low-cost cloud storage services from third parties such as Amazon and Oracle. Data migration between private and public cloud storages will be enabled.
Second, because of extensive use of NoSQL, we plan to provide migration of NoSQL DB as a source and target.
Third, data value analysis technology with analytics. The goal is to automate the proposal of criteria that identify data to be archived through analyzing data usage status.
Samsung SDS striving to develop ILM solutions based on the needs and requirements of the field. We look forward to sharing and developing technologies with companies with great interest in ILM.
▶ The contents are protected by copyrights laws and the copyrights are owned by the creator and Samsung SDS.
▶ Re-use or reproduction as well as commercial use of the contents without prior consent is strictly prohibited.

Jung Jaeho is working for Cloud Architecture Research Team at DB Service Technology Lab of Samsung SDS Research Center. He has experience in Software Engineering, Software Architecture, and Data Architecture. Currently, he is responsible for Samsung SDS ILM solution development and application tech support.
- Zero Trust Security: The Key to Modern Cybersecurity in Cloud Environments | Samsung SDS
- SDSA's Adoption of Cloudability for Superior Cost Management | Samsung SDS
- Innovations in Contents Management to Keep Customers Stay Longer and Visit More Frequently
- Smart Office to Support Business Innovation
- The Chronicles of Cloud Computing
- Finding the Best Cloud Adoption Strategy